Cuproptosis-related gene LIPT1 as a prognostic indicator in non-small cell lung cancer: Functional involvement and regulation of ATOX1 expression
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9931Keywords:
Non-small lung cancer (NSCLC), cuproptosis-related gene, lipoyltransferase 1 (LIPT1), prognostic indicator, antioxidant 1 (ATOX1)Abstract
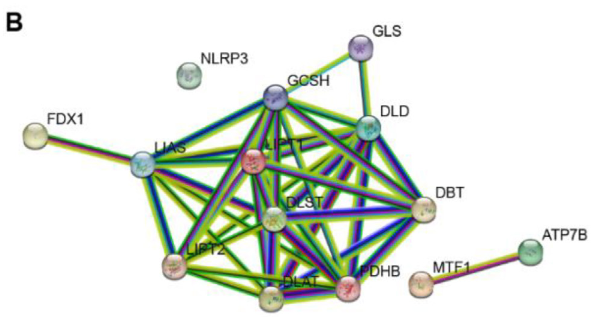
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths, necessitating a deeper understanding of novel cell death pathways like cuproptosis. This study explored the relevance of cuproptosis-related genes in NSCLC and their potential prognostic significance. We analyzed the expression of 16 cuproptosis-related genes in 1017 NSCLC tumors and 578 Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) normal samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to identify significant genes. A risk model and prognostic nomogram were employed to identify the pivotal prognostic gene. Further in vitro experiments were conducted to investigate the functions of the identified genes in NSCLC cell lines. LIPT1, a gene for lipoate-protein ligase 1 enzyme, emerged as the central prognostic gene with decreased expression in NSCLC. Importantly, elevated LIPT1 levels were associated with a favorable prognosis for NSCLC patients. Overexpression of LIPT1 inhibited cell growth and enhanced apoptosis in NSCLC. We confirmed that LIPT1 downregulates the copper chaperone gene antioxidant 1 (ATOX1), thereby impeding NSCLC progression. Our study identified LIPT1 as a valuable prognostic biomarker in NSCLC as it elucidates its tumor-inhibitory role through the modulation of ATOX1. These findings offered insights into the potential therapeutic targeting of LIPT1 in NSCLC, contributing to a deeper understanding of this deadly disease.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ruiyun Deng, Lili Zhu, Jun Jiang, Jing Chen, Hua Li

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-11-15
Published 2024-05-02









