The assessment of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in invasive apocrine carcinoma of the breast in relation to the HER2 status
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9868Keywords:
Breast cancer, special types, apocrine carcinoma, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), HER2-lowAbstract
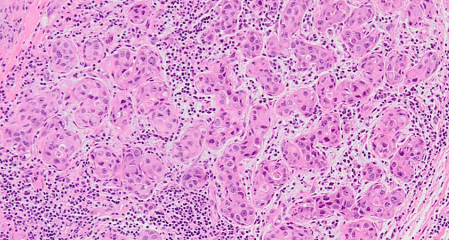
In the current study, we assessed the prevalence and molecular features of HER2-low phenotype in the apocrine carcinomas of the breast (ApoCa) and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). A cohort of 64 well-characterized therapy-naïve ApoCa was used. The TIL distribution was assessed using the hematoxylin and eosin whole slide/scanned images following the international TILs working group recommendations. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) was performed in a subset of HER2-low ApoCa. All patients were women, with a mean age of 62 years. Forty-three carcinomas were pure apocrine carcinoma (PAC; ER−/AR+), and the remaining 21 were classified as apocrine-like carcinomas (ALCs; ER+/−, AR+/−). HER2/neu was positive (score 3+ by IHC and/or amplified by FISH) in 20/43 (47%) PAC and 4/21 (19%) ALC. The prevalence of HER2-low expression (scores 1+ or 2+ without HER2 amplification) in ApoCa was 39% without significant differences between PAC and ALC (P = 0.14); however, the HER2-low phenotype was more prevalent in triple-negative PAC than in ALC (P < 0.001). Levels of TILs were low (≤10%) in 74% of ApoCa (median 5%, range 0%–50%). TIL levels were significantly higher in ALC than in PAC (P = 0.02). HER2 status had no impact on TIL distribution (P = 0.45). The genomic profile of HER2-low ApoCa was similar to other subtypes of ApoCa. ApoCa has predominantly low TIL, particularly PAC. The prevalence of the HER2-low phenotype in ApoCa is high, which should have therapeutic and clinical implications given the recently approved therapies with antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) for HER2-low breast cancers.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Zoran Gatalica, Nataliya Kuzumova, Inga Rose, Monika Ulamec, Melita Peric Balja, Faruk Skenderi, Semir Vranić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









