Efficacy of four anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents and laser treatment for retinopathy of prematurity: A network meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9829Keywords:
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF), aflibercept, bevacizumab, conbercept, ranibizumab, laser therapy, retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), network meta-analysis (NME)Abstract
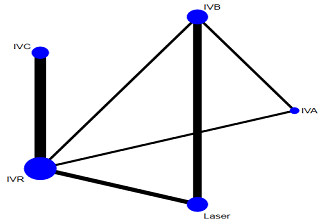
This study undertakes a comprehensive comparison of five different interventions for the treatment of type-1 retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and aggressive posterior ROP (APROP), offering insights into their relative efficacies and contributing to better clinical decision making. The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of intravitreal aflibercept (IVA), intravitreal bevacizumab (IVB), intravitreal conbercept (IVC), intravitreal ranibizumab (IVR), and laser therapy in treating these conditions. We conducted a search for relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in databases, namely, PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Ovid, focusing on these five treatment modalities for ROP. The quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Assessment Tool, and data analysis was performed using STATA software. The results from our network meta-analysis (NMA) indicated that IVA significantly prolonged the interval between initial treatment and relapse in patients, with a surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) value of 99.1%. Additionally, patients in the IVB group had a significantly higher spherical equivalent refraction (SER) after surgery, with a SUCRA value of 84.4%. Furthermore, IVR was the most effective in reducing the duration of peripheral retinal vascularization, with a SUCRA value of 95.6%. However, no statistically significant differences were found in relapse rates among the five treatment options. Our analysis concludes that intravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) drug monotherapy generally offer better outcomes than laser treatment for ROP. Nonetheless, additional RCTs are necessary to further evaluate the safety of anti-VEGF agents.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in this study are available from the corresponding author, Dong Zhou.
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Yufei Xu, Guohua Deng, Jun Zhang, Jie Zhu, Zhinan Liu, Fan Xu, Dong Zhou

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-11-09
Published 2023-11-16









