The protective effect of DNase I in retinal vein occlusion
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9780Keywords:
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO), neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I)Abstract
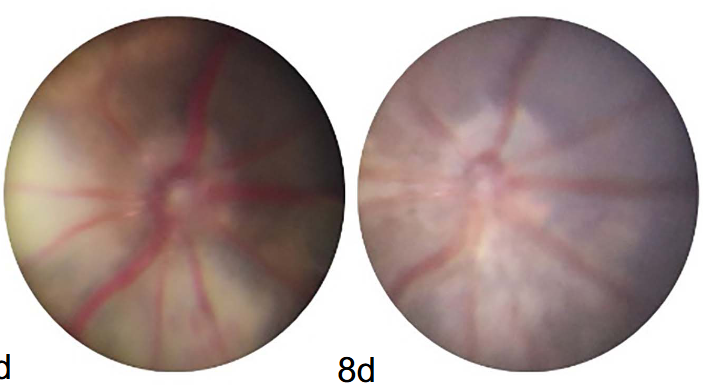
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) ranks as the second most prevalent retinal vascular disease, following diabetic retinopathy. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) play an important role in vascular diseases. This study aimed to elucidate the relationship between NETs and RVO, and to discern the potential role of deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) in the prevention and treatment of RVO through the modulation of NETs. We analyzed circulating NETs biomarkers, namely cell-free DNA (cf-DNA), myeloperoxidase (MPO)-DNA, and neutrophil elastase (NE), in 30 RVO patients and 30 healthy individuals. We established an RVO mouse model using a retinal laser, and the mice were categorized into two groups: the DNase I group and the control group. Retinal images were taken at predetermined time points, and the state of the retinal vessels was assessed. Both tissue and blood samples were harvested for analysis of NETs expression through methods such as western blotting, immunofluorescence staining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Our finding indicate an increase in circulating NETs biomarkers in human and mouse RVO cases, while also verifying the presence of NETs in the retinal thrombus of the RVO model. Both in vitro and in vivo tests revealed that DNase I attenuated NETs formation. Moreover, DNase I injections led to diminished NETs biomarker levels and a reduced duration of the thrombus after the RVO model establishment. Consequently, DNase I, a well-established modulator of NETs formation, might exhibit protective properties in the prevention and treatment of RVO.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Guohua Deng, Xi Zou, Zhinan Liu, Hang Ren, Yanting Li, Bin Chen, Jun Zhang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-10-05
Published 2024-03-11









