Comprehensive analysis of the role of interferon gamma-inducible protein 30 on immune infiltration and prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9693Keywords:
Interferon gamma-inducible protein 30 (IFI30); clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC); immune infiltrationAbstract
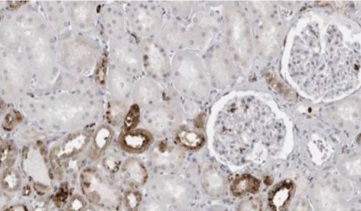
Although the immune factor interferon gamma-inducible protein 30 (IFI30) has been linked to the growth and immune infiltration of various malignancies, its function and mechanism in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) remains unclear. We used several databases to detect and validate IFI30 expression in ccRCC and its connection to immune invasion. We found that IFI30 expression was higher in ccRCC tissues compared to normal tissues, and was strongly associated with tumor grade, T stage, and M stage. Univariate and multivariate analyses showed that ccRCC cases with lower IFI30 expression levels had a higher OS rate than those with high IFI30 expression (P < 0.05). Additionally, we collected a total of 104 cases of ccRCC and adjacent tissues from the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University between January 2018 and January 2020 for immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis, along with their relevant clinicopathological data. The relationship between IFI30 and expression of CD3E, CD4, CD8A, interleukin 10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor beta (TGFB2) was examined using the ccRCC data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, with findings verified by IHC analysis using the collected cases. Statistical analysis performed with SPSS found the positive correlation between the expression of CD3E, CD4, CD8A and IL-10 and the IFI30 expression, and negative correlation of TGFB2 expression with the IFI30 expression in ccRCC. Concurrently, a notable association was observed between high IFI30 expression and immune cell infiltration in ccRCC. High IFI30 expression is connected to the ccRCC's poor prognosis with the infiltration of immune cell. These findings suggest that high IFI30 expression could serve as a marker of poor prognosis and be associated with immune cell infiltration in ccRCC.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Xin Wen, Lei Lei, Fan Wang, Yuan Wang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-11-10
Published 2024-03-11









