Stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease: Bridging the gap between preclinical promise and clinical potential
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9518Keywords:
Stem cells, degenerative disc disease, spine, intervertebral disc regenerationAbstract
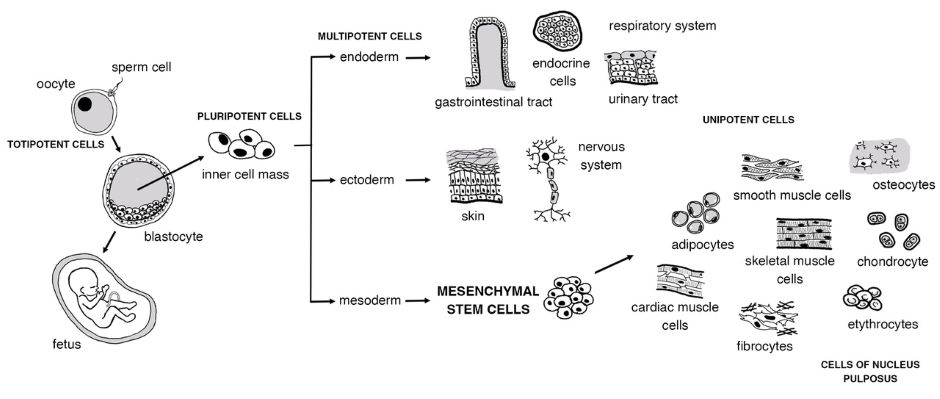
Stem cell therapy has gained attention in the field of regenerative medicine due to its potential to restore damaged tissue. This article focuses on the application of stem cell therapy for treating spinal pathologies, particularly intervertebral disc degeneration. Disc degeneration is a major cause of low back pain and is characterized by changes in the matrix and inflammation. Animal studies have demonstrated that the implantation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) yields promising results, including increased disc height, improved hydration, and reduced inflammation. However, the number of clinical trials remains limited, necessitating further research to optimize MSCs therapy. Although preclinical studies offer valuable insights, caution is needed when extrapolating these findings to clinical practice. Stem cell therapy still faces multiple challenges, such as the durability and survival of MSCs upon implantation, uncertain pathways to discogenic differentiation, and the adverse impact of a harsh microenvironment on cell survival. The avascular nature of the intervertebral disc and dynamic loading conditions also affect the adaptation of transplanted cells. Despite these obstacles, stem cell therapy holds promise as a potential treatment for disc degeneration, and ongoing research aims to fill the current gap in conclusive data.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Matic Munda, Tomaz Velnar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-08-23
Published 2024-03-11









