SKIL/SnoN attenuates TGF-β1/SMAD signaling-dependent collagen synthesis in hepatic fibrosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2023.9000Keywords:
Ski-related novel protein N (SnoN), SKIL, transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), hepatic fibrosis (HF), bioinformaticsAbstract
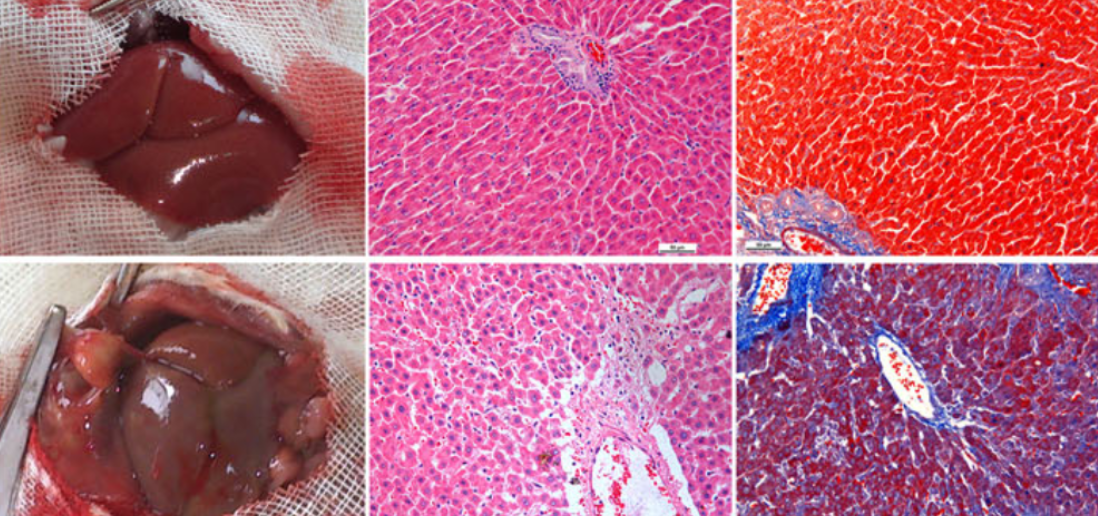
The ski-related novel gene (SnoN), encoded by the SKIL gene, has been shown to negatively regulated transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) signaling pathway. However, the roles of SnoN in hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and hepatic fibrosis (HF) are still unclear. To evaluate the role of SnoN in HF, we combined bulk RNA sequencing analysis and single-cell RNA sequencing analysis to analyse patients with HF. The role of SKIL/SnoN was verified using liver samples from rat model transfected HSC-T6 and LX-2 cell lines. Immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, PCR, and western blotting techniques were used to demonstrate the expression of SnoN and its regulatory effects on TGF-β1 signaling in fibrotic liver tissues and cells. Furthermore, we constructed competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network and potential drug network associated with the SnoN gene. We identified SKIL gene as a differentially expressed gene in hepatic fibrosis. SnoN protein was found to be widely expressed in the cytoplasm of normal hepatic tissues, whereas it was almost absent in HF tissues. In the rat group subjected to bile duct ligation (BDL), SnoN protein expression decreased, while TGF-β1, collagen III, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1), and fibronectin levels increased. We observed the interaction of SnoN with p-SMAD2 and p-SMAD3 in the cytoplasm. Following SnoN overexpression, apoptosis of HSCs was promoted, and the expression of HF-associated proteins, including collagen I, collagen III, and TIMP-1, was reduced. Conversely, downregulation of SnoN inhibited HSC apoptosis, increased collagen III and TIMP-1 levels, and decreased matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13) expression. In conclusion, SnoN expression is downregulated in fibrotic livers, and could attenuate TGF-β1/SMADs signaling-dependent de-repression of collagen synthesis.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Cheng Chi, Xifeng Liang, Tianyu Cui, Xiao Gao, Ruixia Liu, Chenghong Yin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-06-08
Published 2023-11-03









