Echocardiographic and hemodynamic changes in patients with high-grade varicocele
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2022.8854Keywords:
Echocardiography, high-grade varicocele, semen analysis, spermatic vein diameterAbstract
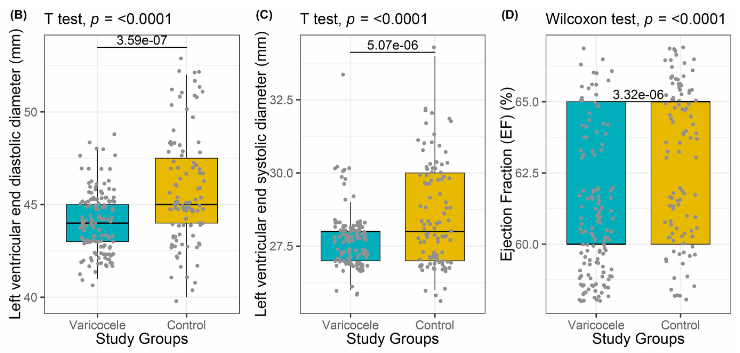
Varicocele is abnormal tortuosity and dilatation of the pampiniform plexus veins within the spermatic cord. Varicocele is associated with testicular atrophy, hypogonadism, impaired semen analysis values, or decreased testosterone production. Varicocele is a progressive disease and should be treated because it may be a systemic disease that can be associated with cardiovascular abnormalities. We hypothesize in this study that cardiovascular and hemodynamic pathologies may occur in varicocele patients. In this prospective, multicentric, multidisciplinary study, patients diagnosed with high-grade left varicocele in the urology clinic underwent semen analysis, total testosterone determination, and scrotal Doppler ultrasonography. In addition, blood pressure measurement and echocardiographic evaluation were performed by blinded cardiologists in both the varicocele patients and the healthy control group. The study was carried out with 103 varicocele patients and 133 healthy individuals who formed the control group. Diastolic blood pressure (P = 0.016), left ventricular end diastolic (P < 0.001) and systolic diameter (P < 0.001), ejection fraction (P < 0.001), pulmonary arterial pressure (P < 0.001), and aortic distensibility (P < 0.001) values were significantly higher in varicocele patients compared with controls; interventricular septum wall thickness (P = 0.022), aortic systolic (P < 0.001) and diastolic diameter (P < 0.001), aortic systolic (P < 0.001) and diastolic diameter index (P < 0.001), and aortic stiffness index (P < 0.001) values were significantly lower in varicocele patients. The mean aortic distensibility of non-normozoospermic group was lower than that of normozoospermic group (P = 0.041). There was no statistically significant relationship between thickest vein diameter in spermatic cord and cardiological parameters. This study showed that symptomatic patients with high-grade varicocele had a higher risk of cardiovascular and hemodynamic disease. We recommend that men with high-grade symptomatic varicocele with impaired semen analysis undergo cardiovascular and hemodynamic evaluation regardless of their spermatic vein diameter.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Batuhan Ergani, Azmi Eyiol, Mustafa Karabiçak, Mesut Gitmez, Muslu Kazım Körez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-02-25
Published 2023-05-01









