Anti-inflammatory role of fenofibrate in treating diseases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2022.8534Keywords:
Fenofibrate, inflammation, mechanism, PPAR-α, diseases, therapyAbstract
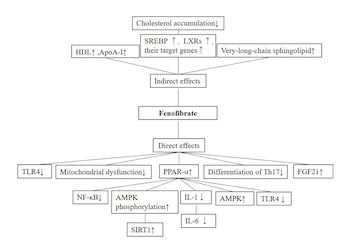
Inflammation contributes to the pathogenesis of several diseases. Fenofibrate, known as a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor - α (PPAR-α) agonist, is a classic drug for treating hyperlipidemia. In addition to its lipid-lowering effect, fenofibrate has also been reported to exert anti-inflammatory effects with complicated underlying mechanisms of action. In general, the anti-inflammatory effect of fenofibrate is secondary to its lipid-lowering effect, especially for the inflammation caused by hyperlipidemia in the circulatory system. Some anti-inflammatory actions may also come from its regulatory effects on intracellular lipid metabolism by activating PPAR-α. In addition, some roles in anti-inflammation might be mediated by its direct regulation of inflammatory signaling pathways. In order to understand anti-inflammatory activities and the underlying mechanisms of fenofibrate action in disease better, we herein reviewed and discussed the anti-inflammatory roles and its subserving mechanisms in various diseases of different organ systems. Thus, this review offers insights into the optimal use of fenofibrate in the clinical setting.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Lv Jin, Hu Hua, Yong Ji, Zhanjun Jia, Mingqi Peng, Songming Huang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-12-26
Published 2023-05-01









