IGHG1 promotes malignant progression in breast cancer cells through the regulation of AKT and VEGF signaling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2022.8508Keywords:
Breast cancer, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), AKT, immunoglobulin heavy constant chain gamma 1 (IGHG1)Abstract
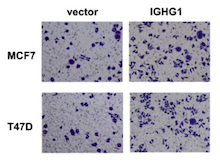
Immunoglobulin heavy constant chain gamma 1 (IGHG1) is highly expressed in a variety of cancers and is considered an emerging prognostic marker. Overexpression of IGHG1 in breast cancer tissues has also been demonstrated, but an in-depth analysis of its role in disease progression has not been explored. In this study, we used a range of molecular and cell-based assays to show that increased expression of IGHG1 in breast cancer cells activates AKT and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling, leading to enhanced cell proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis. We further showed that IGHG1-silencing can suppress the neoplastic characteristics of breast cancer cells in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in nude mice. These data reveal a key role of IGHG1 in the malignant progression of breast cancer cells and highlight its potential as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target to control metastasis and angiogenesis in malignant breast tissue.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Yong Zhang, Xueying Fang, Yan Sun

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-02-20
Published 2023-07-03









