A cuproptosis-associated long non-coding RNA signature for the prognosis and immunotherapy of lung squamous cell carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2022.8481Keywords:
Lung squamous cell carcinoma, cuproptosis, long non-coding RNA, prognosis, immunotherapyAbstract
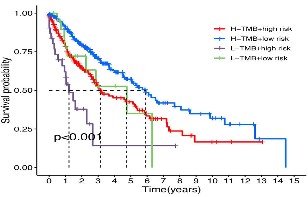
Cuproptosis, a copper-induced mechanism of mitochondrial-related cell death, has been implicated as a breakthrough in the treatment of cancer and has become a new treatment strategy. Furthermore, long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) can change the biological activities of tumor cells. Worldwide, lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) is among the most common annoying tumors. LncRNAs related to cuproptosis are not researched at LUSC. Our research intends to develop a signature on the basis of cuproptosis-associated lncRNAs, which can predict LUSC prognosis and investigate LUSC immunological features. The TCGA database was used to retrieve LUSC transcriptome, clinical, and gene mutation data. For statistical analysis, we utilized the R program. We created a signature consisting of three cuproptosis-related lncRNAs in this investigation (including AC002467.1, LINC01740, and LINC02345). Survival analyses and Receiver Operating Characteristic curves demonstrated that this signature possessed powerful predictive capability. The signature’s ability to predict was confirmed by a Receiver Operating Characteristic curve and principal component analysis. Notably, the patient with a high-risk score and a high tumor mutation burden level had a lower survival time. Furthermore, the tumor immune dysfunction and exclusion analysis showed that these individuals with low-risk scores may benefit from immunotherapy. The signature constructed by three cuproptosis-associated lncRNAs may be prognostic markers of LUSC. It contributes to immunotherapy and offers LUSC’s therapy a new treatment direction.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Chunlan Hou, Xiuping Wu, Caoyang Li, Chao Wang , Jinbo Liu, Qing Luo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2023-01-04
Published 2023-07-03









