PD-L1 testing by immunohistochemistry in immuno-oncology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7953Keywords:
Cancer, immunotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, predictive biomarkers, PD-L1, immunohistochemistryAbstract
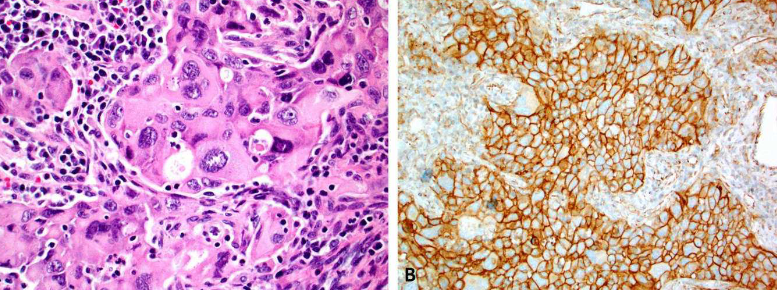
Immunotherapy, based on immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting the Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and/or Programmed Death Receptor 1 (PD-1), has substantially improved the outcomes of patients with various cancers. However, only ~30% of patients benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors. Tumor PD-L1 expression, assessed by immunohistochemistry, is the most widely validated and used predictive biomarker to guide the selection of patients for immune checkpoint inhibitors. PD-L1 assessment may be challenging due to the necessity for different companion diagnostic assays for required specific immune checkpoint inhibitors and a relatively high level of inter-assay variability in terms of performance and cutoff levels. In this review, we discuss the role of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry as a predictive test in immunotherapy (immuno-oncology), highlight the complexity of the PD-L1 testing landscape, discuss various preanalytical, analytical and clinical issues that are associated with PD-L1 assays, and provide some insights into optimization of PD-L1 as a predictive biomarker in immuno-oncology.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Semir Vranic, Zoran Gatalica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









