Relationship between PD-L1 expression and prognostic factors in high-risk cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7574Keywords:
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, PD-L1Abstract
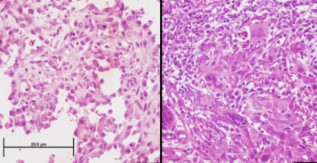
This study aimed to investigate the programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) and basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and its relationship with prognostic factors in tumors that are not in the head and neck region and are therefore relatively less exposed to the sun. This retrospective cross-sectional study included 25 invasive cSCC and 42 BCC cases with a diameter ≥ 2 cm located outside the head and neck region from 2010 to 2018. The biopsy samples were examined based on the membranous PD-L1 (22C3 clone) staining. Staining results were scored as follows: 0, no staining (negative); 1, < 10% PD-L1 positivity of tumor cells; and 2, ≥ 10% PD-L1 positivity of tumor cells. PD-L1 positivity was not seen in any BCC cases, whereas 11 (44%) of cSCC cases were PD-L1 positive. No significant relationship was observed between PD-L1 expression and prognostic parameters, including tumor diameter, tumor depth, and lymphovascular or perineural invasion in the cSCC group. PD-L1 expression was not associated with prognostic factors in the early stages of BCC and SCC located outside the head and neck region. Therefore, investigating the PD-L1 expression seems to be more relevant in patients with advanced-stage disease.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Özden Yülek, Şebnem Batur, Kerem Özcan, Cansu Yol, Övgü Aydın Ülgen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-06-28
Published 2022-10-23









