Circulating cytokine profile and modulation of regulatory T cells in chronic hepatitis B patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7525Keywords:
Chronic hepatitis B, diabetes mellitus, cytokine, interleukin-15, regulatory T cellsAbstract
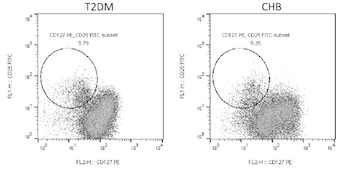
The risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is higher in patients with diabetes mellitus, and diabetes mellitus is one of the metabolic complications of HBV infection. However, the cytokine profile of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is not fully understood. The aim of this study was to investigate the cytokine expression profile in CHB patients with T2DM, and to assess the regulatory function of cytokines to regulatory T cells (Tregs). Forty-four T2DM patients, 39 CHB patients, 17 patients with CHB and T2DM, and 21 control subjects were enrolled. Cytokine levels in the plasma were measured by Luminex multiplex assay. CD4+CD25+CD127dim/- Tregs were detected by flow cytometry. Tregs were purified and stimulated with recombinant human interleukin-15 (IL-15). The regulation of IL-15 on Tregs function was investigated by measuring cell number, IL-10/IL-35 secretion, and mRNA expression of immune checkpoint molecules in a Tregs+PBMC co-culture system. We found that levels of IL-1α, IL-6, and IL-33 were upregulated, while IFN-α, IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 were downregulated in T2DM and CHB patients. CHB patients with T2DM had even lower plasma IL-7 and IL-15 levels. Tregs percentage was elevated in T2DM and CHB patients. CHB patients with T2DM had increased levels of Tregs, which correlated negatively with IL-15. Tregs showed stronger inhibitory activity in CHB patients with T2DM than in controls, T2DM, and CHB patients, which presented as reduction in cellular proliferation and induction of IL-10/IL-35 secretion. IL-15 suppressed Tregs function and inhibited the expression of immune checkpoint molecules in Tregs. The current data suggest that insufficient IL-15 levels and decreased responsiveness of Tregs to IL-15 signaling might contribute to strong immune dysfunction in CHB patients with T2DM.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Wang He, Shu Hao, Xiaohui Dong, Dandan Zhang, Zhen Jia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-06-30
Published 2023-01-06









