Olanzapine decreased osteocyte maturation and Wnt/β-catenin signaling during loading of the alveolar bone in rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7523Keywords:
Olanzapine, osteocyte maturation, bone turnover, bone modeling, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathwa, orthodontic forceAbstract
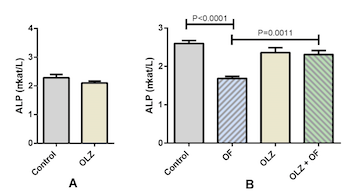
Several studies indicate the influence of olanzapine on bone metabolism; however, the results are contradictory. We evaluated the effects of olanzapine on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, physiological alveolar bone turnover, and alveolar bone modeling due to an applied orthodontic force. Adult male rats (n=48) were treated with either olanzapine or a vehicle for 21 days; then 8 rats from each group were sacrificed and the rest were divided into 4 groups: control, appliance-only, olanzapine-only, and olanzapine-appliance. The rats in the appliance groups were mounted with a superelastic closed coil spring that maintained constant orthodontic force between molars and incisors. We studied the effects of olanzapine on physiological alveolar bone turnover on day 21 of the experiment, and on alveolar bone modeling due to orthodontic force on day 56. We determined tooth movement, alveolar bone volume, activity of bone-specific cells, serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, and gene expression levels of Wnt/β-catenin signaling target genes. During forced bone modeling, olanzapine increased osteoblast volume (P<0.0001) and ALP activity (P=0.0011) and decreased osteoclast volume (P<0.0001) and gene expression of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling target genes Fosl1, Axin2, and Dkk1(P=0.001, P=0.0076, and P=0.036, respectively), and the osteocyte markers Sost and Dmp1 (P=0.0432 and P=0.0021, respectively). Similar results were obtained during physiological alveolar bone turnover on day 21, when olanzapine downregulated the gene expression of osteocyte markers and Wnt/β-catenin signaling target genes. We concluded that olanzapine attenuated osteocyte maturation during forced bone modeling and physiological alveolar bone turnover, potentially through downregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Saranda Disha-Ibrahimi, Borut Furlani, Gorazd Drevenšek, Samo Hudoklin, Janja Marc, Irena Prodan Žitnik, Jakob Sajovic, Martina Drevenšek

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-07-09
Published 2023-01-06









