PLCE1 is a poor prognostic marker and may promote immune escape from osteosarcoma by the CD70-CD27 signaling pathway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7416Keywords:
PLCE1, osteosarcoma, tumor immunity, tumor microenvironment, tumor immune escapeAbstract
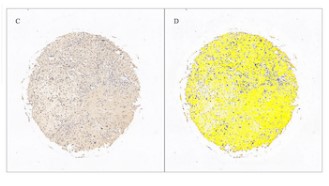
Phospholipase C epsilon 1 (PLCE1) is involved in the pathogenesis of many cancers. However, the biological role of PLCE1 in osteosarcoma (OS) is still poorly understood. The prognostic survival analysis was performed on the PLCE1gene in the TARGET data set and the differential expression of PLCE1 in OS tissue and normal bone tissue on the tissue chip was detected by immunohistochemistry. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient analysis was implemented to explore the relationship between PLCE1 and immune genes. Finally, PLCE1 was silenced to explore its biological function in OS cells. The results of tissue chip immunohistochemistry showed that PLCE1 expression in OS tissue was higher than in normal bone tissue. The survival curve of PLCE1 and its corresponding receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) showed that PLCE1 had a significant effect on the survival status of patients with OS and that the prognosis of patients with high PLCE1 expression was relatively poor. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient analysis and qRT-PCR assays found that PLCE1 may promote immune escape from OS via CD70-CD27 signaling pathway. Silencing of PLCE1 causes the following biological behaviors of OS cells: it promotes apoptosis, inhibits proliferation of OS cells, and inhibits the ability of cell migration and invasion. PLCE1 is a poor prognostic marker and a potential key factor affecting the immune status of the OS tumor microenvironment.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Linhai Huang, Chundi Liao, Hanhua Wu, Piwei Huang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-05-29
Published 2022-10-23









