Genetic risk factors in melanoma etiopathogenesis and the role of genetic counseling: A concise review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.7378Keywords:
Melanoma, Genetics, hereditary syndrome, genetic counsellingAbstract
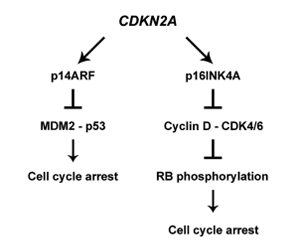
Melanoma is a highly aggressive cancer originating from melanocytes. Its etiopathogenesis is strongly related to genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. Melanomas encountered in clinical practice are predominantly sporadic, whereas hereditary melanomas account for approximately 10% of the cases. Hereditary melanomas mainly develop due to mutations in the CDKN2A gene, which encodes two tumor suppressor proteins involved in the cell cycle regulation. CDKN2A, along with CDK4, TERT, and POT1 genes, is a high-risk gene for melanoma. Among the genes that carry a moderate risk are MC1R and MITF, whose protein products are involved in melanin synthesis. The environment also contributes to the development of melanoma. Patients at risk of melanoma should be offered genetic counseling to discuss genetic testing options and the importance of skin UV protection, avoidance of sun exposure, and regular preventive dermatological examinations. Although cancer screening cannot prevent the development of the disease, it allows for early diagnosis when the survival rate is the highest.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Nikola Serman, Semir Vranic, Mislav Glibo, Ljiljana Serman, Zrinka Bukvic Mokos

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









