ORM 1 as a biomarker of increased vascular invasion and decreased sorafenib sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2022.7268Keywords:
ORM1, microvascular invasion, sorafenib sensitivity, hepatocellular carcinomaAbstract
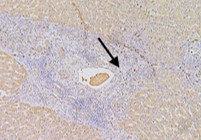
This study aimed to clarify the role of Orosomucoid 1 (ORM1) in the development and therapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The mRNA expression level of ORM1 was analyzed via integrative analysis of Gene Express Omnibus (GEO) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) datasets. The protein expression level of ORM1 in our cohort was determined using immunohistochemistry. Correlation analysis was used to investigate the relationship between ORM1 expression and clinical parameters. The Cell Counting Kit-8 assay was used to clarify the role of ORM1 in HCC malignant behaviors, including cell growth and sorafenib sensitivity, in vitro. The results indicated that ORM1 was significantly downregulated in the hepatic cancer cells compared to that in the non-cancerous cells. However, it was upregulated in microvascular invasion samples, especially in the cancer embolus compared to that in the surrounding tumor cells. Though Kaplan-Meier analysis did not show an association of ORM1 expression with the overall survival rates of HCC patients, univariate analysis indicated that ORM1 expression was highly correlated with tumor grade and stage. An in vitro assay also revealed that downregulation of ORM1 led to the suppression of tumor growth and enhancement of sorafenib sensitivity without epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) alteration, which was consistent with our bioinformatic analysis. Hence, ORM1 played a key role in HCC tumorigenesis and may serve as a potential target for the development of therapeutics against HCC in the future.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Jiangning Gu, Shiqi Xu, Xiang Chen, Haifeng Luo, Guang Tan, Wenjing Qi, Feng Ling, Chenqi Wang, Feiliyan Maimaiti, Yunlong Chen, Lili Yang, Menghong Yin, Dan Chen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-06-03
Published 2022-10-23









