The impact of vitamin and mineral supplements usage prior to COVID-19 infection on disease severity and hospitalization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.7009Keywords:
COVID-19, supplements, vitamin D, hospitalization, severityAbstract
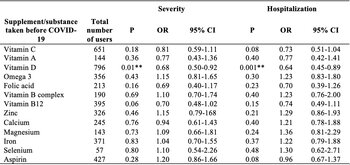
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a global public health emergency. Nutritional status is suggested to be related to the severity of COVID-19 infection. Herein, we aimed to explore the impact of using vitamin and mineral supplements prior to COVID-19 infection on disease severity and hospitalization. In addition, the prior use of aspirin as an anticoagulant on the disease severity was investigated. A cross-sectional, self-administered survey was conducted between March and July 2021. Recovered COVID-19 individuals (age ≥ 18 years, n = 2148) were recruited in the study. A multivariate logistic regression was used to evaluate the associations of supplements and aspirin use with COVID-19 disease severity and hospitalization status. Among the participants, 12.1% reported symptoms consistent with severe COVID-19, and 10.2% were hospitalized due to COVID-19. After adjustment for confounding variables (age, gender, BMI, cigarette smoking status, and the number of comorbidities), the multivariate logistic regression model showed that the consumption of vitamin D supplements prior to COVID-19 infection was associated with a significant decrease in disease severity (OR = 0.68, 95% CI 0.50 - 0.92; P = 0.01), and a lower risk of hospitalization (OR = 0.64, 95% CI 0.45 - 0.89; P = 0.01). On the other hand, there were no significant differences in the frequencies of severe illness and hospitalizations with the consumption of vitamin A, folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin B complex, vitamin C, zinc, iron, selenium, calcium, magnesium, omega 3, and aspirin before COVID-19 infection. Among the investigated nutrients, the use of vitamin D prior to COVID-19 infection was associated with reduced disease severity and hospitalization. However, more studies are required to confirm this finding.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Refat Nimer, Omar Khabour, Samer Swedan, Hassan Kofahi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2022-02-19
Published 2022-09-16









