Reconstruction of intestinal microecology of type 2 diabetes by fecal microbiota transplantation: Why and how
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.6323Keywords:
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation, intestinal microecology, type 2 diabetesAbstract
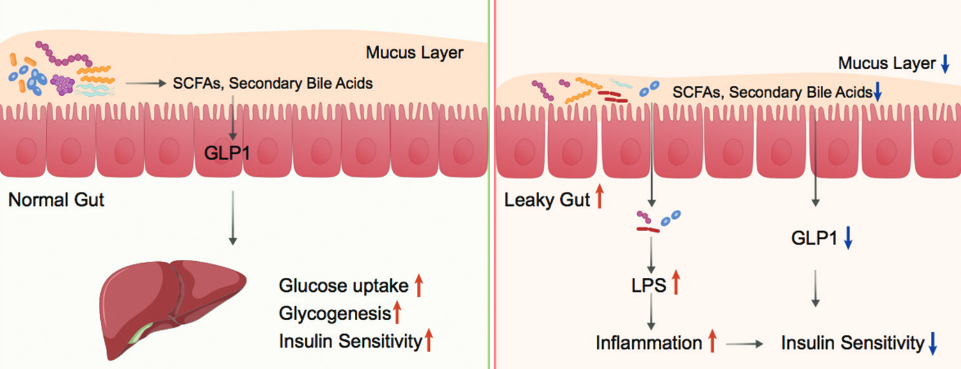
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance. Mounting evidence has correlated T2D to alterations in the composition of gut microbiota. Accordingly, targeting the gut microbiota has become an emerging strategy for T2D management. The aim of this article is to get a better insight into the rationale for targeting gut microbiota in T2D treatment. Thus, we herein reviewed the change of gut microbiota composition in T2D, factors shaping gut microbiota, and potential mechanisms behind the contribution of gut microbiota to T2D pathogenesis. At present, it has become possible to use intestinal microorganism capsules, bacteria liquid, and other preparations to carry out fecal microbiota transplantation for the treatment and intervention of T2D with insulin resistance and immune-mediated type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Zhe-Sheng Chen, Chuanxing Xiao

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2021-10-13
Published 2022-06-01









