A novel ferroptosis-related gene signature can predict prognosis and influence immune microenvironment in acute myeloid leukemia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2021.6274Keywords:
Acute myeloid leukemia, ferroptosis, prognostic gene signature, overall survival, tumor immune microenvironment, drug resistanceAbstract
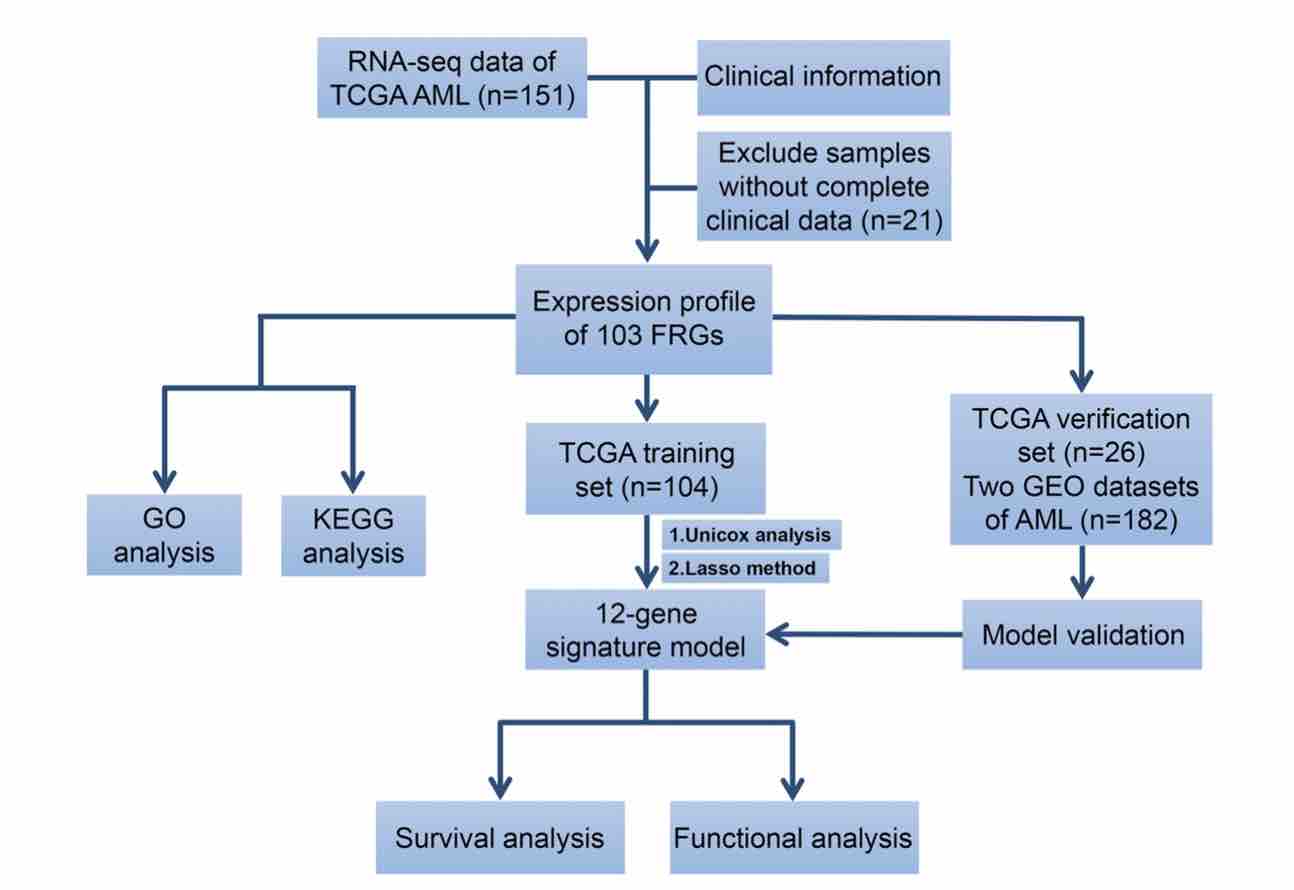
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a highly heterogeneous hematopoietic malignancy that strongly correlates with poor clinical outcomes. Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent, non-apoptotic form of regulated cell death which plays an important role in various human cancers. Nevertheless, the prognostic significance and functions of ferroptosis-related genes (FRGs) in AML have not received sufficient attention. The aim of this article was to evaluate the association between FRGs levels and AML prognosis using publicly available RNA-sequencing datasets. The univariate Cox regression analysis identified 20 FRGs that correlate with patient overall survival. The LASSO Cox regression model was used to construct a prognostic 12-gene risk model using a TCGA cohort, and internal and external validation proved the signature efficient. The 12-FRGs signature was then used to assign patients into high- and low-risk groups, with the former exhibiting markedly reduced overall survival, compared to the low-risk group. ROC curve analysis verified the predictive ability of the risk model. Functional analysis showed that immune status and drug sensitivity differed between the 2 risk groups. In summary, FRGs is a promising candidate biomarker and therapeutic target for AML.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Xianbo Huang, De Zhou, Xiujin Ye, Jie Jin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2021-11-11
Published 2022-07-29









