Different dose-dependent effects of ebselen in sciatic nerve ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2015.521Keywords:
Ebselen, ischemia-reperfusion injury, oxidative stress, sciatic nerve.Abstract
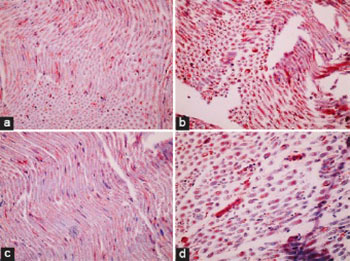
Ebselen is an organoselenium compound which has strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. We investigated the neuroprotective role of ebselen pretreatment in rats with experimental sciatic nerve ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. Adult male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into four groups (N = 7 in each group). Before sciatic nerve I/R was induced, ebselen was injected intraperitoneally at doses of 15 and 30 mg/kg. After a 2 h ischemia and a 3 h reperfusion period, sciatic nerve tissues were excised. Tissue levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO), and activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase (CAT) were measured. Sciatic nerve tissues were also examined histopathologically. The 15 mg/kg dose of ebselen reduced sciatic nerve damage and apoptosis (P < 0.01), levels of MDA, NO, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) positive cells (P < 0.01, P < 0.05, respectively), and increased SOD, GPx, and CAT activities (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, P < 0.05, respectively) compared with the I/R group that did not receive ebselen. Conversely, the 30 mg/kg dose of ebselen increased sciatic nerve damage, apoptosis, iNOS positive cells (P < 0.01, P < 0.05, P < 0.001) and MDA and NO levels (P < 0.05, P < 0.01) and decreased SOD, GPx, and CAT activities (P < 0.05) compared with the sham group. The results of this study suggest that ebselen may cause different effects depending on the dose employed. Ebselen may be protective against sciatic nerve I/R injury via antioxidant and antiapoptotic activities at a 15 mg/kg dose, conversely higher doses may cause detrimental effects.
Citations
Downloads
References
Gholami MR, Abolhassani F, Pasbakhsh P, Akbari M, Sobhani A, Eshraghian MR, et al. The effects of simvastatin on ischemia-reperfusion injury of sciatic nerve in adult rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2008;590:111-4.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.05.050
Bagdatoglu OT, Polat G, Bagdatoglu C, Atik U. Effects of peripheral nerve ischemia-reperfusion model on serum cytokine levels. Turk Neurosurg 2008;18:149-56.
Iida H, Schmeichel AM, Wang Y, Schmelzer JD, Low PA. Orchestration of the inflammatory response in ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2007;12:131-8.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8027.2007.00132.x
Nagamatsu M, Schmelzer JD, Zollman PJ, Smithson IL, Nickander KK, Low PA. Ischemic reperfusion causes lipid peroxidation and fiber degeneration. Muscle Nerve 1996;19:37-47.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mus.880190103
Weisfeldt ML. Reperfusion and reperfusion injury. Clin Res 1987;35:13-20.
Schewe T. Molecular actions of ebselen--an antiinflammatory antioxidant. Gen Pharmacol 1995;26:1153-69.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0306-3623(95)00003-J
Azad GK, Tomar RS. Ebselen, a promising antioxidant drug: mechanisms of action and targets of biological pathways. Mol Biol Rep 2014;41:4865-79.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3417-x
Institute for Laboratory Animal Research, National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press; 2010: 248.
Ledesma JC, Font L, Aragon CM. The H2O2 scavenger ebselen decreases ethanol-induced locomotor stimulation in mice. Drug Alcohol Depend 2012;124:42-9.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.12.003
Koizumi H, Fujisawa H, Suehiro E, Shirao S, Suzuki M. Neuroprotective effects of ebselen following forebrain ischemia: involvement of glutamate and nitric oxide. Neurol Med Chir 2011;51:337-43.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2176/nmc.51.337
Sayan H, Ozacmak VH, Ozen OA, Coskun O, Arslan SO, Sezen SC, et al. Beneficial effects of melatonin on reperfusion injury in rat sciatic nerve. J Pineal Res 2004;37:143-8.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2004.00145.x
Yagi K. Simple assay for the level of total lipid peroxides in serum or plasma. Methods Mol Biol 1998;108:101-6.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1385/0-89603-472-0:101
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 1982;126:131-8.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-X
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 1988;34:497–500.
Paglia DE, Valentine WN. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 1967;70:158-69.
Johansson LH, Borg LA. A spectrophotometric method for determination of catalase activity in small tissue samples. Anal Biochem 1988;174:331-6.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(88)90554-4
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976;72:248-54.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Coban YK, Ciralik H, Kurulas EB. Ischemic preconditioning reduces the severity of ischemia-reperfusion injury of peripheral nerve in rats. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj 2006; 1:2.
Schmelzer JD, Zochodne DW, Low PA. Ischemic and reperfusion injury of rat peripheral nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1989;86:1639-42.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.5.1639
Nagamatsu M, Schmelzer JD, Zollman PJ, Smithson IL, Nickander KK, Low PA. Ischemic reperfusion causes lipid peroxidation and fiber degeneration. Muscle Nerve 1996;19:37-47.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mus.880190103
Coskun O, Yuncu M, Kanter M, Buyukbas S. Ebselen protects against oxidative and morphological effects of high concentration chronic toluene exposure on rat nerves. Eur J General Med 2006;3:64-72.
Gul S, Bahadir B, Hanci V, Acikgoz S, Bektas S, Ugurbas E, et al. Effects of ebselen versus nimodipine on cerebral vasospasm subsequent to experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Clin Neurosci 2010;17:608-11.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2009.07.115
Aras M, Altas M, Meydan S, Nacar E, Karcıoglu M, Ulutas KT, et al. Effects of ebselen on ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat brain. Int J Neurosci 2014;124:771-6.
http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2013.879581
Bredt DS, Snyder SH. Nitric oxide: a physiologic messenger molecule. Annu Rev Biochem 1994;63:175-95.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.001135
Endoh M, Maiese K, Wagner J. Expression of the inducible form of nitric oxide synthase by reactive astrocytes after transient global ischemia. Brain Res 1994;651:92-100.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(94)90683-1
Poderoso JJ, Carreras MC, Lisdero C, Riobó NA, Schöpfer F, Boveris A. Nitric oxide inhibits electron transfer and increases superoxide radical production in rat heart mitochondria and submitochondrial particles. Arch Biochem Biophys 1996; 328: 85–92.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1996.0146
Porciúncula LO, Rocha JB, Cimarosti H, Vinadé L, Ghisleni G, Salbego CG, et al. Neuroprotective effect of ebselen on rat hippocampal slices submitted to oxygen-glucose deprivation: correlation with immunocontent of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Neurosci Lett 2003;346:101-4.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(03)00580-9
Wei L, Zhang Y, Yang C, Wang Q, Zhuang Z, Sun Z. Neuroprotective effects of ebselen in traumatic brain injury model: involvement of nitric oxide and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2014;41:134-8.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12186
Warner DS, Sheng H, Batinić-Haberle I. Oxidants, antioxidants and the ischemic brain. J Exp Biol 2004;207:3221-31.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01022
Unsal C, Oran M, Albayrak Y, Aktas C, Erboga M, Topcu B, et al. Neuroprotective effect of ebselen against intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress in rats. Toxicol Ind Health 2013;14. [Epub ahead of print].
http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0748233713509429
Kalayci M, Coskun O, Cagavi F, Kanter M, Armutcu F, Gul S, Acikgoz B. Neuroprotective effects of ebselen on experimental spinal cord injury in rats. Neurochem Res 2005;30:403-10.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-2615-2
Freude B, Masters TN, Robicsek F, Fokin A, Kostin S, Zimmermann R, et al. Apoptosis is initiated by myocardial ischemia and executed during reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2000;32:197-208.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmcc.1999.1066
Yamagata K, Ichinose S, Miyashita A, Tagami M. Protective effects of ebselen, a seleno-organic antioxidant on neurodegeneration induced by hypoxia and reperfusion in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Neuroscience 2008;153:428-35.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.02.028
Yoshizumi M, Kogame T, Suzaki Y, Fujita Y, Kyaw M, Kirima K, et al. Ebselen attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via the inhibition of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase and activator protein-1 signalling pathway in PC12 cells. Br J Pharmacol 2002;136:1023-32.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0704808
Yang CF, Shen HM, Ong CN. Ebselen induces apoptosis in HepG(2) cells through rapid depletion of intracellular thiols. Arch Biochem Biophys 2000;37:142-52.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1999.1574
Xu JH, Hu HT, Liu Y, Qian YH, Liu ZH, Tan QR, et al. Neuroprotective effects of ebselen are associated with the regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in cultured mouse cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 2006;399(3):210-4.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2006.02.024
Paunesku T, Mittal S, Protić M, Oryhon J, Korolev SV, Joachimiak A, et al. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): ringmaster of the genome. Int J Radiat Biol 2001;77:1007-21.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09553000110069335
Louis DN, Edgerton S, Thor AD, Hedley-Whyte ET. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen and Ki-67 immunohistochemistry in brain tumors: a comparative study. Acta Neuropathol 1991;81:675-9.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00296379
Ino H, Chiba T. Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in the adult and developing mouse nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2000;78:163-74.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0169-328X(00)00092-9
Deng X, Wei H, Lou D, Sun B, Chen H, Zhang Y, et al. Changes in CLIP3 expression after sciatic nerve injury in adult rats. J Mol Histol 2012;43:669-79.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9450-y
Shi H, Liu S, Miyake M, Liu KJ. Ebselen induced C6 glioma cell death in oxygen and glucose deprivation. Chem Res Toxicol 2006;19:655-60.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx0502544
Yang CF, Shen HM, Ong CN. Intracellular thiol depletion causes mitochondrial permeability transition in ebselen-induced apoptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys 2000;380:319-30.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/abbi.2000.1939
Gogvadze V, Klein SD, Shigenaga M, Ames BN, Richter C. Effect of ebselen on Ca2+ transport in mitochondria. Redox Rep 2000;5:359-63.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2015-06-06
Published 2015-08-26









