Assessment of Wnt pathway selected gene expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of postmenopausal patients with low bone mass
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.5179Keywords:
Osteoporosis, Wnt pathway, PBMC, expression, BMD, fracturesAbstract
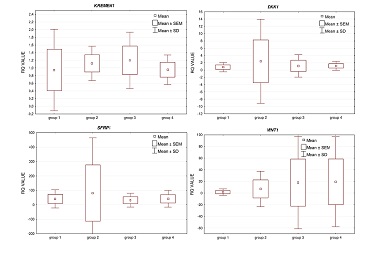
The purpose of the study was to assess the expression of selected genes of the Wnt pathway: APC, AXIN1, CTNNB1, DKK1, GSK3β, KREMEN1, SFRP1, and WNT1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of patients, selected in consideration of their bone mineral density (BMD), and the occurrence of low-energy fractures. The study involved 45 postmenopausal women, divided into four groups, according to BMD and fracture history. Measurements of laboratory parameters and RNA expression in PBMC cells were carried out in material, collected once at the inclusion visit. The densitometric examination was performed on all participants. In the analysis of the relative expression levels (RELs) of the studied genes in the entire population, we observed an overexpression for SFRP1 in 100% of samples and WNT1. In addition, the REL of DKK1, APC, and GSK3β genes were slightly elevated versus the calibrator. In contrast, CTNNB1 and AXIN1 presented with a slightly decreased RELs. Analysis did not show any significant differences among the groups in the relative gene expression levels (p < 0.05) of particular genes. However, we have observed quite numerous interesting correlations between the expression of the studied genes and BMD, the presence of fractures, and laboratory parameters, both in the whole studied population as well as in selected groups. In conclusion, the high level of CTNNB1 expression maintains normal BMD and/or protects against fractures. It also appears that the changes in expression levels of the Wnt pathway genes in PBMCs reflect the expected changes in bone tissue.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-12-17
Published 2021-08-01









