Clinical applications of avian eggshell-derived hydroxyapatite
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.4888Keywords:
Bone tissue regeneration, eggshell, guided bone regeneration, hydroxyapatite, socket preservationAbstract
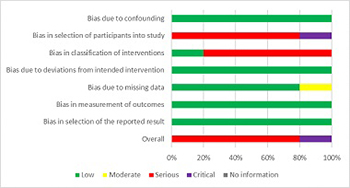
The search for bone reconstruction materials and methods is an ongoing challenge. The aim of this review is to systemically search the available literature concerning the clinical performance of eggshell as a substitute material in guided bone regeneration in oral surgery. Five databases (PubMed, Cochrane, Web of Science, Scopus, and Embase) were searched up to February 2020. Clinical trials that used eggshell as a bone substitute material were included in the review. Animal and in vivo studies were excluded from the review. ROBINS-I was used to evaluate the risk of bias. A total of 840 studies were retrieved, out of which 55 full-text articles were screened. Five studies were finally included: one study showed critical and four serious risk of bias. A total of 74 patients and 88 intervention sites were included in the five studies. Clinical and radiological evaluation showed complete healing during the follow-ups. Statistically significant radiological and clinical evidence of new bone formation was achieved for socket preservation, grafting after third molar extraction, and cystic/apicectomy grafting. One patient with complications was reported. Histological analysis and micro computed tomography confirmed that it promotes bone regeneration. A comparison with synthetic hydroxyapatite showed similar healing characteristics. Within the limitations of the included studies, the eggshell can be safely and efficiently used in guided bone regeneration procedures, but more research is needed to completely evaluate the full potential of this material.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-07-04
Published 2020-11-02









