Long non-coding RNA PVT1 regulates the migration of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells via miR-3619-5p/MKL1 axis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2020.4641Keywords:
PVT1, miR-3619-5p, MKL1, cell migration, hepatocellular carcinoma, HCCAbstract
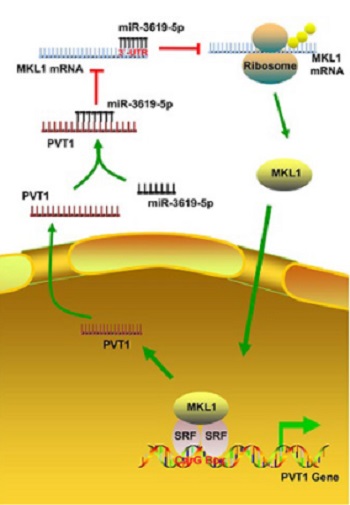
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third most common malignant tumor of the digestive system. Plasma cell tumor heterotopic gene 1 (PVT1) is an intergenic long non-coding RNA that is aberrantly expressed in different cancers. Myocardin-related transcription factor A or megakaryoblastic leukemia 1 (MKL1) is a transcriptional coactivator of serum response factor that has been shown to promote cancer cell migration and invasion. In this study, we investigated the relationship between PVT1 and MKL1 as a novel regulatory mechanism underlying HCC progression. We used HepG2 and Cos‑7 cell lines. Transfection experiments with miR-3619-5p mimics/inhibitor, PVT1, siRNA-PVT1, MKL1, or siRNA-MKL1 were performed. RNA and protein levels were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription PCR and Western blot, respectively. Cell migration was assessed by transwell assay. Luciferase assays, RNA-FISH, RNA immunoprecipitation, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were performed to confirm the interaction between PVT1, miR-3619-5p, and MKL1 in HCC cells. Overexpression of PVT1 was positively correlated with MKL1 upregulation, which promoted HepG2 cell migration. miR-3619-5p inhibited MKL1 expression in HCC cells by acting on its 3′-UTR. Furthermore, PVT1 promoted MKL1 expression and migration in HCC cells by directly binding to miR-3619-5p. In a positive feedback loop, MKL1 could activate PVT1 transcription by binding to the CArG box in the promoter region. Our findings may provide a basis for the development of novel targeted therapies in HCC.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-02-22
Published 2021-04-01









