Diagnostic performance of LI-RADS version 2018 in differentiating hepatocellular carcinoma from other hepatic malignancies in patients with hepatitis B virus infection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4576Keywords:
Hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, ICCA, combined HCC-cholangiocarcinoma, cHCC-CCA, hepatitis B virus, HBV, Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS)Abstract
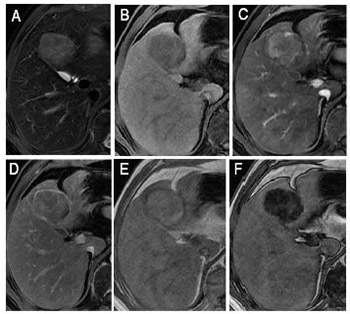
The diagnostic performance of the Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) in differentiating hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from other hepatic malignancies has not been investigated in Chinese patients with chronic liver disease from hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The aim of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of the LI-RADS version 2018 in differentiating HCC, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICCA), and combined HCC-cholangiocarcinoma (cHCC-CCA) in Chinese patients with HBV infection. Seventy consecutive HBV-infected patients with ICCA (n = 48) or cHCC-CCA (n = 22) who underwent contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) between 2006 and 2017 were enrolled along with a comparison cohort of 70 patients with HCC and CE-MRI-matched for tumor size (10–19 mm, 20–30 mm, 31–50 mm, and >50 mm). Imaging feature frequencies for each tumor type were compared using Fisher’s exact test. The classification accuracy of LR-5 and LR-M was estimated for HCC versus non-HCC (ICCA and cHCC-CCA). The interobserver agreement was good for LI-RADS categories of HCC and moderate for non-HCC. After consensus read, 66 of 70 (94%) HCCs were categorized LR-5 (including tumor in vein [TIV] with LR-5), while 42 of 48 (88%) ICCAs and 13 of 22 (59%) cHCC-CCAs were categorized LR-M (including TIV with LR-M) (p < 0.001). Thus, assignment of LR-5 provided 94% sensitivity and 81% specificity for HCC. LR-M provided 79% sensitivity and 97% specificity for non-HCC (ICCA and cHCC-CCA); and the sensitivity and accuracy were lower in differentiating HCC from non-HCC (tumor size <20 mm). LI-RADS v2018 category 5 and M reliably differentiated HBV-related HCC from ICCA. However, a substantial proportion of cHCC-CCAs were categorized LR-5 rather than LR-M. While management is controversial for these combined tumors, accurate prospective differentiation is desired for optimal treatment.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-01-19
Published 2020-08-03









