Effects of TCF7L2 rs7903146 variant on metformin response in patients with type 2 diabetes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4181Keywords:
Metformin, type 2 diabetes, pharmacogenetics, transcription factor 7-like 2 gene, TCF7L2Abstract
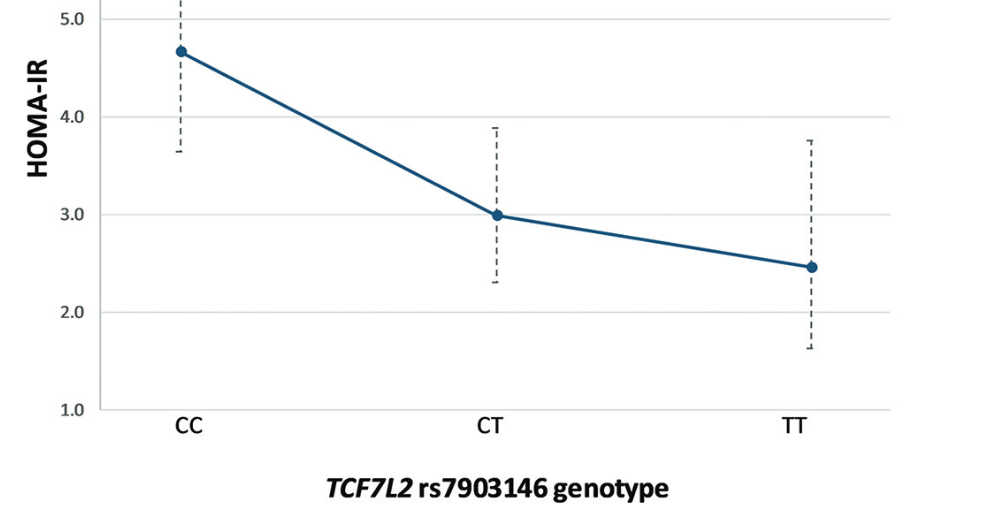
The response to metformin, the most commonly used drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D), is highly variable. The common variant rs7903146 C>T within the transcription factor 7-like 2 gene (TCF7L2) is the strongest genetic risk factor associated with T2D to date. In this study, we explored the effects of the TCF7L2 rs7903146 genotype on metformin response in T2D. The study included 86 newly diagnosed patients with T2D, incident users of metformin. Levels of fasting glucose, insulin, HbA1c, total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, and anthropometric parameters were measured prior to metformin therapy, and 6 and 12 months after the treatment. Genotyping of the TCF7L2 rs7903146 was performed by the Sequenom MassARRAY® iPLEX® platform. At baseline, the diabetes risk allele (T) showed an association with lower triglyceride levels (p = 0.037). After 12 months of metformin treatment, the T allele was associated with 25.9% lower fasting insulin levels (95% CI 10.9–38.3%, p = 0.002) and 29.1% lower HOMA-IR index (95% CI 10.1–44.1%, p = 0.005), after adjustment for baseline values. Moreover, the T allele was associated with 6.7% lower fasting glucose levels (95% CI 1.1–12.0%, p = 0.021), adjusted for baseline glucose and baseline HOMA-%B levels, after 6 months of metformin treatment. This effect was more pronounced in the TT carriers who had 16.8% lower fasting glucose levels (95% CI 7.0–25.6%, p = 0.002) compared to the patients with CC genotype. Our results suggest that the TCF7L2 rs7903146 variant affects markers of insulin resistance and glycemic response to metformin in newly diagnosed patients with T2D within the first year of metformin treatment.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Association of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-04-05
Published 2019-11-08









