Age- and gender-independent association of glutathione S-transferase null polymorphisms with chronic myeloid leukemia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4176Keywords:
GSTs, glutathione S-transferase, null polymorphism, GSTT1, GSTM1, CML, haplotypeAbstract
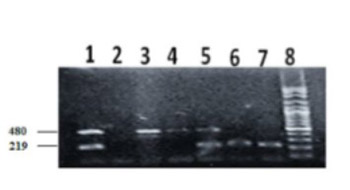
The glutathione S-transferase (GST) genes encode enzymes that mediate the detoxification of xenobiotics by catalyzing the conjugation of glutathione (GSH) to xenobiotic substrates. The aim of the current study is to investigate the association between GSTT1 and GSTM1 polymorphisms and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) among Sudanese patients. Patients with CML (n = 115) were recruited to the study from the Radiation and Isotope Centre Khartoum (RICK)-Sudan. Healthy individuals (n = 104) were included as controls. Genotyping of GSTT1 and GSTM1 polymorphisms was performed using multiplex PCR. Null deletions in the GSTT1 and GSTM1 genes are common in the Sudanese population (control group), with frequencies of 33.9% and 38.2%, respectively. The frequencies of GSTT1 (OR: 3.25, 95% CI: 1.87–5.65, p < 0.001) and GSTM1 (OR: 2.14, 95% CI: 1.25–3.67, p < 0.005) null genotypes were significantly higher in CML patients vs. controls. The distribution of GSTT1 and GSTM1 null polymorphisms was not different between male and female (p > 0.01) and young and old CML patients (p > 0.05). Hematological parameters were not affected by null polymorphisms in the patient group (p > 0.05). In addition, the frequency of GSTM1 null polymorphism was lower in advanced-phase CML patients compared to chronic-phase patients (p < 0.05). The GSTT1 and GSTM1 null polymorphisms are associated with CML among Sudanese patients, independently of their age and gender.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-03-11
Published 2019-04-15









