Isoflurane exposure in infant rats acutely increases aquaporin 4 and does not cause neurocognitive impairment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.4116Keywords:
Anesthesia, aquaporin 4 (AQP4), neurocognition, infant rat, isoflurane, pediatric anesthesia, 10-day-old ratAbstract
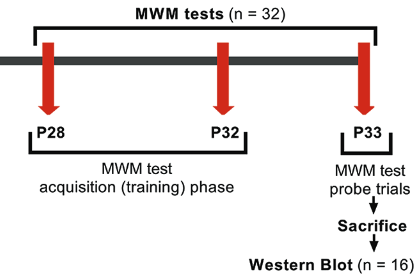
Isoflurane is commonly used in pediatric population, but its mechanism of action in cognition is unclear. Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) regulates water content in blood, brain, and cerebrospinal fluid. Various studies have provided evidence for the role of AQP4 in synaptic plasticity and neurocognition. In this study, we aimed to determine whether a prolonged exposure to isoflurane in infant rats is associated with cognition and what effect this exposure has on AQP4 expression. Ten-day-old [postnatal day (P) 10] Wistar albino rats were randomly allocated to isoflurane group (n = 32; 1.5% isoflurane in 50% oxygen for 6 hours) or control group (n = 32; only 50% oxygen for 6 hours). Acute (P11) and long-term (P33) effects of 6-hour anesthetic isoflurane exposure on AQP4 expression were analyzed in whole brains of P11 and P33 rats by RT-qPCR and Western blot. Spatial learning and memory were assessed on P28 to P33 days by Morris Water Maze (MWM) test. The analysis revealed that isoflurane increased acutely both mRNA (~4.5 fold) and protein (~90%) levels of AQP4 in P11 rats compared with control group. The increasing levels of AQP4 in P11 were not observed in P33 rats. Also, no statistically significant change between isoflurane and control groups was observed in the latency to find the platform during MWM training and probe trial. Our results indicate that a single exposure to isoflurane anesthesia does not influence cognition in infant rats. In this case, acutely increased AQP4 after isoflurane anesthesia may have a protective role in neurocognition.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2019-02-19
Published 2019-08-20









