Effects of epinephrine on heart rate variability and cytokines in a rat sepsis model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2018.3565Keywords:
Sepsis, heart rate variability, HRV, epinephrine, EPI, inflammation, β-blocker, ratsAbstract
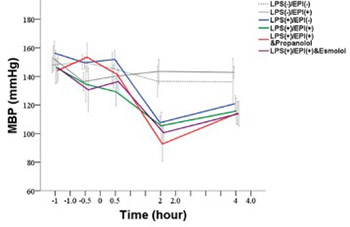
Catecholamines have both anti-inflammatory and vasoactive properties. A decreased cardiac response to catecholamines has been associated with a high risk of death in sepsis and septic shock. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of epinephrine (EPI) on heart rate variability (HRV) and autonomic balance, as well as cytokine levels, in a rat sepsis model. Thirty-six male Sprague-Dawley rats were assigned to 4 experimental groups and 2 control groups of 6 rats each. The rats in the experimental groups were inoculated with a lipopolysaccharide (LPS, endotoxin) to establish a sepsis model. Group A received only LPS; group B received LPS, antecedent EPI and the nonselective β-blocker propranolol; group C received LPS and antecedent EPI; and group D received LPS, antecedent EPI and the selective β1-blocker esmolol. One control group received EPI and the other received saline placebo. Heart rate variability (HRV) was analyzed and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) levels were measured. Measurements were carried out at baseline, at 0 hour after EPI infusion, and at 0.5, 2, and 4 hours after LPS inoculation. There were significant differences in HRV and cytokine levels between the groups, indicating that LPS infusion caused autonomic imbalance. Antecedent EPI significantly decreased the level of TNF-α in group C compared with group A in which TNF-α level peaked at 2 hours and then declined. Propranolol (group B) but not esmolol (group D) administration resulted in elevated TNF-α levels, comparable to those observed in group A. In conclusion, antecedent administration of EPI in a rat sepsis model inhibits the production of TNF-α possibly via the β2-adrenoceptor.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-06-06
Published 2020-02-05









