Urinary System Birth Defects in Surgically Treated Infants in Sarajevo Region of Bosnia and Herzegovina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2008.2965Keywords:
congenital anomalies, urinary system, frequency, sex distributionAbstract
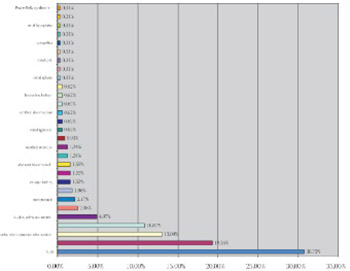
Congenital anomalies of the urinary system are relatively common anomalies. In Bosnia and Herzegovina there is no existent unique evidence of congenital anomalies and registries. The aim of this study was to obtain the frequency of different urinary tract anomalies types and their sex distribution among cases hospitalized in the Department of Pediatric Surgery of the University of Sarajevo Clinics Centre, Bosnia and Herzegovina, during the period from January 2002 to December 2006. Retrospective study was carried out on the basis of clinical records. Standard methods of descriptive statistics were performed for the data analysis. Among 289 patients that were surgically treated 62,37% of the patients were male patients, while 37,63% were female patients. Twenty nine different urinary system anomalies types were found in this study. These were: vesicoureteral reflux (99 cases or 30,75%), hypospadias (62 cases or 19,26%), pelviureteric junction obstruction (42 cases or 13,04%), megaureter (35 cases or 10,87%), duplex pelvis and ureter (16 cases or 4,97%), bladder diverticulum (8 cases or 2,48%), ureterocoele (7 cases or 2,17%), stenosis of the external urethral opening (6 cases or 1,86%), ectopic kidney, duplex kidney and pelvis (each 5 cases or 1,55%), polycystic kidneys and urethral stricture (each 4 cases or 1,24%), multicystic kidney (3 cases or 0,93%), kidney agenesis, ureter agenesis, urethral diverticulum, ectopic ureter, horseshoe kidney and fetal kidney (each 2 cases or 0,62%), renal aplasia, urethral atresia, renal cyst, urachal cyst, epispadias, bladder exstrophy, renal hypoplasia, renal malrotation and Prune-Belly syndrome (each 1 case or 0,31%). According to this study, urinary tract anomalies were more common in male than in female patients (62,37%), Generally, the most frequent anomaly type was vesicoureteral reflux in total number of 99 cases, and in females (66 cases), but hypospadias was the most common anomaly in males (62 cases). The anomalies of other systems associated with urinary system anomalies were found in ten cases. These were: cryptorchidism, congenital inguinal hernia, open inner inguinal ring, uterus bicornis unicollis and one case of multiple anomalies.
Citations
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-01-14
Published 2008-05-20









