Epidemiologic Genotyping of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2008.2930Keywords:
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, infection control, pulsed field gel electrophoresisAbstract
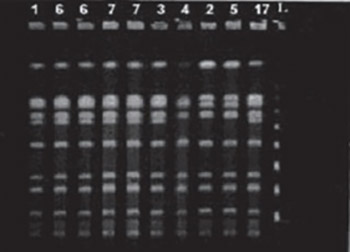
čćStaphylococcus aureus has long been recognized as one of the leading cause of hospital infections all over the world. Increased frequency of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in hospitalized patients and possibility of vancomycin resistance requires rapid and reliable characterization of isolates and control of MRSA spread in hospitals. Typing of isolates helps to understand pathogenesis and route of the hospital pathogen spread. In this study in the analysis of an outbreak of MRSA infections in one surgical ward, we used pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) as a method of typing. PFGE revealed one epidemic strain type A in 13 out of 16 patients, and another two types (type B in two patients and type C in one patient). Discussing the typing results in the ward has changed the admission policy of patients with infected vascular ulcers who were then cured as outpatients, and admitted for surgery after that. This policy resulted with the stopping of the outbreak; during next 2,5 year there was no further MRSA outbreak in the ward. PFGE also showed subtypes which enabled the insight into dynamics of MRSA strain changes during the outbreak. PFGE could be recommended as a screening method in the MRSA outbreak analysis. Because of it’s high discriminatory power still remains the gold standard for MRSA typing
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-01-04
Published 2008-08-20









