Evaluation of Risk Markers Fluctuation During an Initial Therapy with Rosiglitazon in Patients Suffering from Metabolic Syndrome
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2009.2788Keywords:
metabolic syndrome, HbA1C, risk-markers, diabetics, prediabeticsAbstract
The aim of this study was to examine the effects of hypoglycaemic drug-agonists of PPAR-gama recep- tors-rosiglitazone (Avandia,4 mg - Glaxo Smith Kline) on values of wide-spread risk-markers: fibrinogen, C-reactive protein and uric acid and glicolysated haemoglobin HbA1C as parameter of metabolic control. We examined forty patients who satisfied criteria for metabolic syndrome and distributed them into groups of diabetic and prediabetic patients according to criteria of IDF (International Diabetic Federation).
These risk markers and glicolysated haemoglobin HbA1C were observed at the beginning of therapy, then four, eight and twelve weeks into therapy and results were compared and statistically processed.
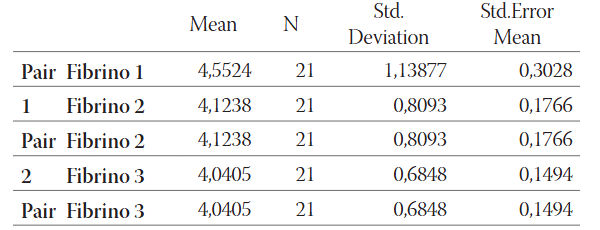
Three months initial therapy with rosiglitazone significantly reduced values of HbA1C, fibrinogen and CRP but not uric acid in prediabetic patients.
Rosiglitazone initial three months therapy significantly reduced HbA1C, fibrinogen and uric acid, but not CRP in diabetic patients.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-12-07
Published 2009-11-20









