The effects of hypoglycemic and alcoholic coma on the blood-brain barrier permeability
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2011.2591Keywords:
blood-brain barrier, hypoglycemic coma, alcoholic comaAbstract
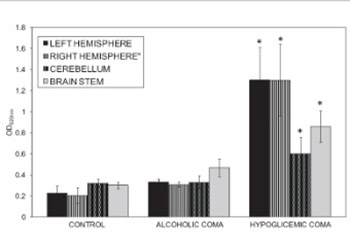
In this investigation, the effects of hypoglycemic coma and alcoholic coma on the blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability have been compared. Female adult Wistar albino rats weighing 180-230 g were divided into three groups: Control group (n=8), Alcoholic Coma Group (n=18), and Hypoglycemic Coma group (n=12). The animals went into coma approximately 3-4 hours after insulin administration and 3-5 minutes after alcohol administration. Evans blue (4mL/kg) was injected intravenously as BBB tracer. It was observed that the alcoholic coma did not significantly increase the BBB permeability in any of the brain regions when compared to control group. Changes in BBB permeability were significantly increased by the hypoglycemic coma in comparison to the control group values (p<0.01). Our findings suggest that hypoglycemic and alcoholic coma have different effects on the BBB permeability depending on the energy metabolism.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-10-21
Published 2011-05-20









