The hepatic protective mechanism of Ginkgo biloba extract in rats with obstructive jaundice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2011.2547Keywords:
cholestasis, hepatic injury, endothelin 1, nitric oxide, ginkgo biloba extractAbstract
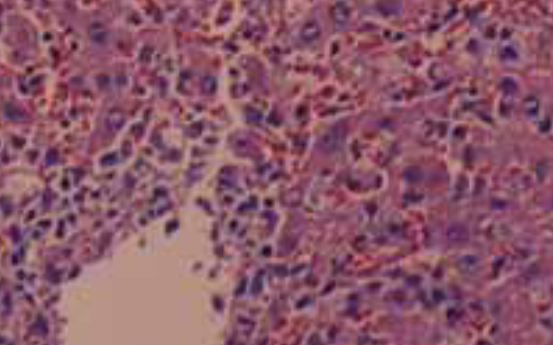
The objective of our study was to examine the hepatic protective mechanism of Ginkgo biloba extract (GBE) in rats with obstructive jaundice (OJ). Twenty rats underwent bile duct ligation and received daily intraperitoneal injections of either control saline or Ginkgo biloba extract for 14 days. Ten sham-operated rats had their bile duct exposed but not ligated or sectioned. Serum alanine transaminase (ALT) was analyzed for liver function tests and liver damage was further assessed by histologic examination. The levels of endothelin 1 (ET-1) and nitric oxide (NO) in blood and liver homogenate were measured. The serum alanine transaminase was elevated in the bile duct ligation rats (BDL rats); GBE could significantly lower serum transaminase level and ameliorate liver histological damage. ET-1 and NO levels in both plasma and liver tissue were also elevated in common bile duct (CBD)-ligated rats, but this increase was significantly decreased by GBE treatment. Moreover, the degree of liver damage severity positively correlates with high levels of ET-1 and NO. GBE mediated the liver protective effect at least in part by suppressing overproduction of ET-1and NO and restoring a proper balance between ET-1and NO to some extent.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-10-10
Published 2011-11-20









