Chewing gums has stimulatory effects on bowel function in patients undergoing cesarean section: A randomized controlled trial
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2012.2452Keywords:
bowel function, chewing gums, cesarean sectionAbstract
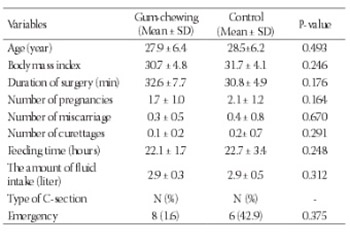
The aim of study was to investigate the effect of postoperative gum chewing on the recovery of bowel function after cesarean section. Total 100 women delivered by lower uterine segment section cesarean under local anesthesia (spinal). Eligible patients were randomly allocated into two groups: a gum-chewing group (n=50) or a control group (n= 50). The gum-chewing group participants who received one stick of sugarless gum for one hours, three times daily immediately after recovery from anesthesia and the control group had the usual postoperative care until being discharged. All women were followed up regularly until discharge from hospital, and recorded the times to the first bowel sounds of normal intestinal sounds, the time to the first passage of flatus, the time to the first feeling of hunger, and the time to the first defecation. The operative data, postoperative tolerance of gum chewing, and postoperative complications were documented. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of demographic characteristics such as age, body mass index, parity, duration of surgery, number of miscarriages and curettages, time to the first feeding, the amount of serum intake, and type of cesarean section. The mean average postoperative interval of the first bowel sounds (21.9 versus 26.1 hours, p= 0.016), the first feeling of hunger (11.8 versus 14.5 hours, p= 0.050), the first passage of flatus (24.8 versus 30.0 hours, P=0.002), the first defecation (30.6 versus 38.4 hours, P= 0.0001) was significantly shorter compared to the control group.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-09-14
Published 2012-11-20









