Effect of co-administration of morphine and nicotine on cardiovascular function in two-kidney one clip hypertensive (2K1C) rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2013.2345Keywords:
baroreflex sensitivity, blood pressure, nitric oxide, morphine, nicotineAbstract
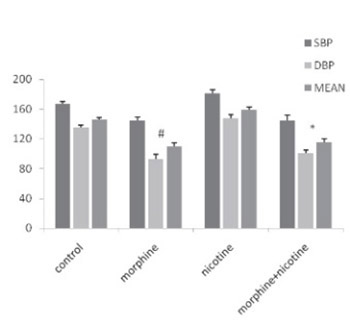
Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality are potentiated with smoking and hypertension. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of morphine and nicotine co-administration on cardiovascular function in two-kidney one-clip hypertensive (2K1C) rats. Thirty-two male rats were divided into four groups as follow: Vehicle, morphine, nicotine and nicotine + morphine. All drugs were administered for 8 weeks. Baroreflex sensitivity (BRS), heart rate and blood pressure were measured using a Power Lab data acquisition. Plasma rennin activity (PRA) and serum concentration of nitric oxide (NO) were measured using Elisa method. To induce hypertension, the renal artery of left kidney was clipped for 8 weeks. A significant decrease in systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) was observed in nicotine + morphine group compared to vehicle and nicotine groups (p<0.05). Serum concentration of NO was lower in nicotine + morphine group compared to morphine group and significantly higher than nicotine group. The BRS was lower in the nicotine + morphine group compared to other groups. The PRA level was higher in nicotine + morphine compared to morphine group but it was higher than nicotine group. This study demonstrated that prolonged co-consumption of morphine and nicotinedecreased PRA and blood pressure and increased the serum concentration of NO in hypertensive rats. Co-administration of morphine and nicotine decreased BRS in 2kic hypertensive rats probably via central nervous system.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-08-09
Published 2013-08-20









