Advancing regenerative therapies with umbilical cord–derived mesenchymal stem cells: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.13147Keywords:
Regenerative medicine, clinical studies, immunomodulation, anti-inflammatory therapy, tissue repair and regenerationAbstract
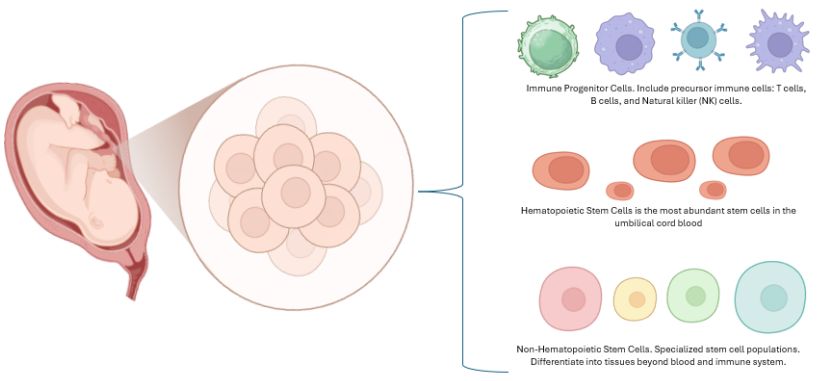
Umbilical cord–derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) are a clinically attractive regenerative and immunomodulatory platform that combines ethical accessibility, low immunogenicity, rapid expansion, genetic stability, and a potent paracrine secretome. This study aimed to synthesize evidence on safety, efficacy, and translational readiness by conducting a focused PubMed review (2014–2024) restricted to clinical studies and trials, using predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria and structured data extraction. Across indications, UC-MSCs show a consistent safety profile and signals of benefit mediated by tissue repair and immune regulation: in musculoskeletal disease they improve osteoarthritis pain and function and may slow osteonecrosis; in hepatology they sustain gains in decompensated cirrhosis, mitigate acute allograft rejection, and aid recovery from ischemic-type biliary lesions; as induction in renal transplantation they are feasible with early graft benefits; in type 2 diabetes responders improve glycemic control and inflammation, while maternal and obstetric factors can shape intrinsic cell properties; in neurology, studies in cerebral palsy, chronic spinal cord injury, and traumatic optic neuropathy report motor, sensory, and visual improvements; in COVID-19–related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) trials show better oxygenation, radiological recovery, quality of life, and modulation of the TNF–sTNFR2 axis; in immune-mediated and transplant settings they reduce graft-versus-host disease, with signals in systemic lupus erythematosus, refractory immune thrombocytopenia, Crohn’s fistulas, and as cotransplant support in aplastic anemia. The limitations of this study encompass small sample sizes, single-center designs, and short-duration trials. Additionally, there is significant heterogeneity concerning the source, manufacturing processes, dosage, administration routes, and endpoints. Other challenges include adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP), issues related to potency, biobanking, logistical constraints, cost factors, and regulatory obstacles. Large multicenter randomized trials with standardized protocols and long-term follow-up, and combination strategies with biomaterials, gene engineering, and extracellular vesicle or exosome products, are needed to confirm durable benefit and enable routine clinical integration.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mohamed Hussein

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









