Hormonal predictors of the insulin sensitive phenotype in humans
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12210Keywords:
Obesity, adipokines, gut hormones, body contouring surgery, insulin sensitivity, pancreatic polypeptide, PP, gastric inhibitory polypeptide, GIP, leptin, liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2, LEAP2Abstract
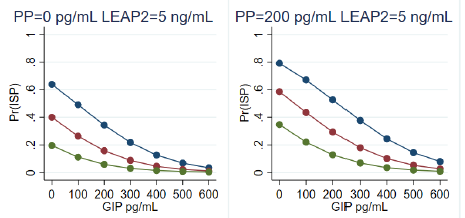
Clinical obesity, a chronic condition marked by excessive fat accumulation, often leads to insulin resistance and a heightened risk of comorbidities. This study aimed to identify hormonal predictors of an insulin-sensitive phenotype (ISP) in patients undergoing body contouring surgeries, focusing on the relationship between gut hormones, adipokines, and fat mass. ISP was defined as the highest tertile of HOMA insulin sensitivity. We prospectively followed patients undergoing abdominoplasty, lower body lift, or thigh lift at Hamad General Hospital from January 2021 to December 2023. Body composition, glycemic indices, and hormonal levels were assessed, with data analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression models. The study included 34, 22, and 27 subjects at visits 1, 2, and 3, respectively. Fat percentage decreased slightly at visits 2 and 3 compared to baseline, though not significantly. Median levels of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), pancreatic polypeptide (PP), liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (LEAP2), and amylin varied significantly across visits, initially rising at visit 2 before declining at visit 3. Logistic regression revealed that ISP was negatively associated with serum GIP. LEAP2, and leptin levels while positively associated with PP. History of bariatric surgery was only weakly associated with the ISP after hormonal associations were accounted for. Notably, total body fat percentage did not predict ISP after accounting for hormonal factors. This study highlights GIP, PP, leptin, and LEAP2 as key predictors of ISP, with GIP being the primary negative regulator. These findings underscore the importance of hormonal interplay in insulin sensitivity, emphasizing the role of gut hormones and adipokines in predicting ISP in humans.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mohamed Badie Ahmed, Abdella M. Habib, Saif Badran, Abeer Alsherawi, Sherouk Essam Elnefaily, Mansour Binfayed, Atalla Hammouda, Graeme E. Glass, Ibrahem Abdalhakam, Abdul-Badi Abou-Samra, Suhail A. Doi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









