Hyomental distance in the different head positions and hyomental distance ratio in predicting difficult intubation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2016.1217Keywords:
Laryngoscopy, Airway, Difficult intubation, Hyoid bone, Chin, The hyomental distance ratioAbstract
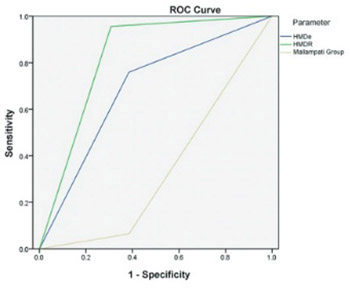
The hyomental distance ratio (HMDR) is the ratio between the hyomental distance (HMD) (the distance between the hyoid bone and the tip of the chin) at the extreme of head extension (HMDe) and the one in the neutral position (HMDn). The objective of the study was to examine the predictive value, sensitivity, and specificity of HMDe, HMDn, and HMDR in predicting difficult endotracheal intubation (DI). A prospective study included 262 patients that underwent elective surgical operations. The following parameters were observed as possible predictors of DI: HMDR, HMDe, HMDn, Mallampati score, and body mass index (BMI). The cut-off points for the DI predictors were HMDe <5.3 cm, HMDn ≤5.5 cm, and HMDR ≤1.2. The assessment that DI existed was made by the anesthesiologist while performing laryngoscopy by applying the Cormack-Lehane classification. DI was present in 13 patients (5%). No significant difference was observed in the frequency of DI with regard to the sex, age, and BMI of the patients. Our research indicated HMDR as the best predictor of DI with a sensitivity of 95.6% and specificity of 69.2%. HMDR can be used in the everyday work of anesthesiologists because HMDR values ≤1.2 may reliably predict DI.
Citations
Downloads
References
. Wilson ME, Spiegelhalter D, Robertson JA, Lesser P. Predicting difficult intubation. Br J Anaesth 1988;61(2):211-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bja/61.2.211.
. Kalezić N, Milosavljević R, Paunović I, Živaljević V, Diklić A, Matić D, et al. The incidence of difficult intubation in 2000 patients undergoing thyroid surgery-singlecenter experience. Vojnosanit Pregl 2009;66(5):377-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.2298/VSP0905377K.
. Noppens RR. Airway management in the intensive care unit. Acta Clin Croat 2012;51(3):511-7.
. Calder I, Calder J, Crockard HA. Difficult direct laryngoscopy in patients with cervical spine disease. Anaesthesia 1995;50(9):756-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1995.tb06135.x.
. Juvin P, Lavaut E, Dupont H, Lefevre P, Demetriou M, Dumoulin JL, et al. Difficult tracheal intubation is more common in obese than in lean patients. Anesth Analg 2003;97(2):595-600. http://dx.doi.org/10.1213/01.ANE.0000072547.75928.B0.
. Takenaka I, Iwagaki T, Aoyama K, Ishimura H, Kadoya T. Preoperative evaluation of extension capacity of the occipitoatlantoaxial complex in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison between the Bellhouse test and a new method, hyomental distance ratio. Anesthesiology 2006;104(4):680-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200604000-00011.
. Huh J, Shin HY, Kim SH, Yoon TK, Kim DK. Diagnostic predictor of difficult laryngoscopy: The hyomental distance ratio. Anesth Analg 2009;108(2):544-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1213/ane.0b013e31818fc347.
. Wojtczak JA. Submandibular sonography: Assessment of hyomental distances and ratio, tongue size, and floor of the mouth musculature using portable sonography. J Ultrasound Med 2012;31(4):523-8.
. Samsoon GL, Young JR. Difficult tracheal intubation: A retrospective study. Anaesthesia 1987;42(5):487-90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1987.tb04039.x.
. Cormack RS, Lehane J. Difficult tracheal intubation in obstetrics. Anaesthesia 1984;39(11):1105-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1984.tb08932.x.
. Rose DK, Cohen MM. The airway: Problems and predictions in 18,500 patients. Can J Anaesth 1994;41:372-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03009858.
. Rao ST, Gowda V. Hyomental distance ratio as a diagnostic predictor of difficult laryngoscopy. Indian J Appl Res 2013;3(8):511-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.15373/2249555X/AUG2013/161.
. Honarmand A, Safavi M, Ansari N. A comparison of between hyomental distance ratios, ratio of height to thyromental, modified Mallamapati classification test and upper lip bite test in predicting difficult laryngoscopy of patients undergoing general anesthesia. Adv Biomed Res 2014;3:166. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.139130.
. Lee A, Fan LT, Gin T, Karmakar MK, NganKee WD. A systematic review (meta-analysis) of the accuracy of the Mallampati tests to predict the difficult airway. Anesth Analg 2006;102(6):1867-78. http://dx.doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000217211.12232.55.
. Shiga T, Wajima Z, Inoue T, Sakamoto A. Predicting difficult intubation in apparently normal patients: A meta-analysis of bedside screening test performance. Anesthesiology 2005;103(2):429-37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200508000-00027.
. Yildiz TS, Korkmaz F, Solak M, Toker K, Erciyes N, Bayrak F, et al. Prediction of difficult tracheal intubation in Turkish patients: A multi-center methodological study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2007;24(12):1034-40.http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S026502150700052X.
. Kheterpal S, Martin L, Shanks AM, Tremper KK. Prediction and outcomes of impossible mask ventilation: A review of 50,000 anesthetics. Anesthesiology 2009;110(4):891-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e31819b5b87.
. Mashour GA, Kheterpal S, Vanaharam V, Shanks A, Wang LY, Sandberg WS, et al. The extended Mallampati score and a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus are predictors of difficult laryngoscopy in the morbidly obese. Anesth Analg 2008;107(6):1919-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1213/ane.0b013e31818a9946.
. Ittichaikulthol W, Chanpradub S, Amnoundetchakorn S, Arayajarernwong N, Wongkum W. Modified Mallampati test and thyromental distance as a predictor of difficult laryngoscopy in Thai patients. J Med Assoc Thai 2010;93(1):84-9.
. Fritscherova S, Adamus M, Dostalova K, Koutna J, Hrabalek L, Zapletalova J, et al. Can difficult intubation be easily and rapidly predicted? Biomed Pap Med FacUnivPalacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2011;155(2):165-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.5507/bp.2011.032.
. Perez-Santos FJ, Hernandez-Salgado M, Diaz-Landeira J, Santana Dominguez M, Dominguez-Garcia J, Herrera-Garcia M. Usefulness of difficult airway predictors in the emergency department. Emergencias 2011;23:293-8.
. Lundstrøm LH, Vester-Andersen M, Møller AM, Charuluxananan S, L'hermite J, Wetterslev J, et al. Poor prognostic value of the modified Mallampati score: A meta-analysis involving 177 088 patients. Br J Anaesth 2011;107(5):659-67. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bja/aer292.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2016-05-02
Published 2016-08-02









