Role of Fascin-1 in cervical cancer metastasis via Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12114Keywords:
Fascin-1, cervical cancer, CC, activating Wnt/β-catenin pathwayAbstract
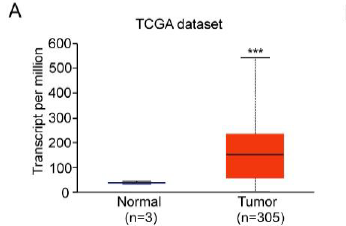
This investigation delves into the impact of Fascin-1, a protein known for its role in actin bundling and its association with metastatic enhancement, on the advancement of cervical cancer (CC). Elevated levels of Fascin-1 have been observed in metastatic carcinomas, but its impact on gene regulation in CC has not been thoroughly studied. Our research demonstrates a marked elevation in the expression of Fascin-1 within tissues affected by CC. Experiments employing both overexpression and knockdown methods revealed that Fascin-1 plays a critical role in promoting the proliferation and mobility of CC cells in vitro. Correspondingly, reducing Fascin-1 levels led to a marked decrease in tumor growth and metastatic spread in vivo. At the molecular level, diminishing Fascin-1 expression resulted in decreased β-catenin and C-myc RNA and protein levels. This implies that Fascin-1 could intensify the progression of CC by influencing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade. This study not only elucidates the mechanism by which Fascin-1 contributes to the advancement of CC but also proposes a novel approach for therapeutic intervention.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yan Wang, Wei Cui, Dong-Mei Chu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









