Profiling of sesquiterpenoid fractions from Artemisia annua L. and testing their in vitro anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.12052Keywords:
Alpha variant SARS-CoV-2, antiviral activity, arteannuin B, Artemisia annua L, countercurrent chromatography, supercritical fluid extractionAbstract
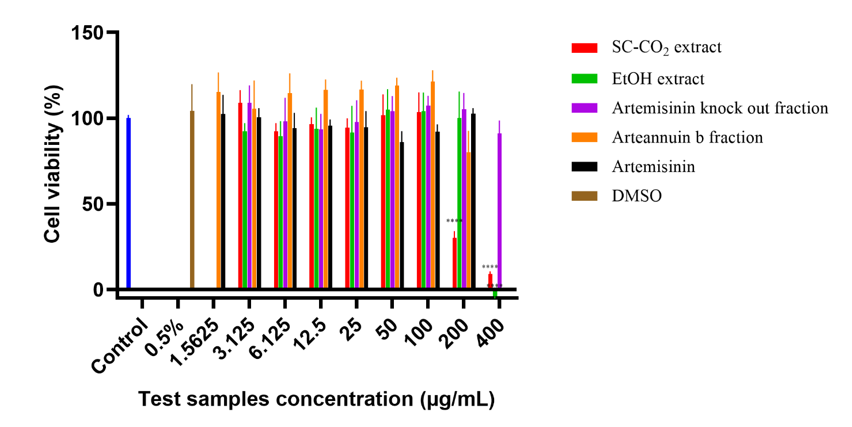
The current state of research on the anti‑SARS‑CoV‑2 potential of artemisinin‑related compounds has identified arteannuin B as a potent inhibitor of the nCoV‑2019BetaCov/Wuhan/WiV04/2019 and BetaCov/Italy/CDG1/2020 strains of the virus. The aim of this work was to fractionate the targeted sesquiterpenoid compounds, arteannuin B and artemisinin, from the complex matrix of the crude ethanolic leaf extract of Artemisia annua L. using high‑speed countercurrent chromatography (HSCCC) and to test the simplified or purified fractions against the genomically characterized Alpha SARS‑CoV‑2 variant in vitro. This is the first detailed in vitro anti‑SARS‑CoV‑2 study using an analytically characterized supercritical fluid extract of A. annua L. The preparative HSCCC method enabled the isolation of purified arteannuin B in a single chromatographic step, which was confirmed by LC‑ESI‑QTOF‑MS/MS. The MS data confirmed the selectivity of the HSCCC method for the targeted fractionation of artemisinin from the complex matrix, as it was successfully separated from the EtOH crude extract without co‑elution with arteannuin B. Antiviral activity determined by quantitative real‑time PCR (qRT‑PCR) yielded half‑maximal effective concentrations (EC₅₀) of 93.7 µg/mL (SC‑CO₂ extract), 173.5 µg/mL (EtOH extract), 187.3 µg/mL (artemisinin knockout fraction), 38.1 µg/mL (arteannuin B fraction), and >100 µg/mL (artemisinin). The arteannuin B fraction was highly active at 50 µg/mL (p < 0.0001) and 100 µg/mL (p < 0.0001), and inhibited the amplification of the SARS‑CoV‑2 N and RdRp genes by 84% and 100%, respectively. An important contribution of this study is the demonstration of the antiviral activity of arteannuin B against the Alpha variant of SARS‑CoV‑2, which is known to have increased infectivity and transmissibility.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Irma Gušić, Ilma Terzić, Toni Eterović, Adis Softić, Šejla Goletić, Teufik Goletić, Dejan Nikolić, Emina Korić, Katarina Bijelić, Haris Nikšić, Senka Vidović, Kemal Durić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









