Atypical presentation of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Clinical and radiological characteristics in eclamptic patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2016.1201Keywords:
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, magnetic resonance, computed tomography, brain, vasogenic edemaAbstract
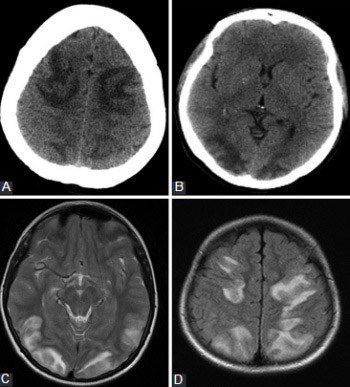
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is an obstetric emergency frequently occurring in a pregnant or puerperal woman, manifested with an acute headache, consciousness impairment, seizures, and visual deficits and is associated with white matter changes predominantly affecting the posterior parietal and occipital lobes of the brain. Apart from the above-described typical location of the changes, the most common atypical location involves the brain stem and basal ganglia. Since magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more sensitive and specific imaging technique compared to computerized tomography, establishing the diagnosis and follow-up in patients with PRES is based mainly on MRI findings. It is particularly important not to exclude PRES as a possible diagnosis when we have the appropriate clinical presentation accompanied by the atypical radiological findings, since this clinical-radiological syndrome can often be manifested with an atypical MRI image.
Citations
Downloads
References
Oyinloye OI, Adesiyun OA, Atobatele MO, Fawole AA. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a adult female. Ann Afr Med 2014;13(3):138-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/1596-3519.134422.
Wagner SJ, Acquah LA, Lindell EP, Craici IM, Wingo MT, Rose CH, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and eclampsia: Pressing the case for more aggressive blood pressure control. Mayo Clin Proc 2011;86(9):851-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.4065/mcp.2011.0090.
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 1996;334(8):494-500. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199602223340803.
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF. Distinct imaging patterns and lesion distribution in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2007;28(7):1320-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0549.
Nakagawa K, Sorond FA, Ropper AH. Ultra-early magnetic resonance imaging findings of eclampsia. Arch Neurol 2008;65(7):974-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archneur.65.7.974.
Bartynski WS. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 1: Fundamental imaging and clinical features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29(6):1036-42. http://dx.doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0928, http://dx.doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0929.
Schwartz RB, Feske SK, Polak JF, DeGirolami U, Iaia A, Beckner KM, et al. Preeclampsia-eclampsia: Clinical and neuroradiographic correlates and insights into the pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy. Radiology 2000;217(2):371-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiology.217.2.r00nv44371.
Cipolla MJ. Cerebrovascular function in pregnancy and eclampsia. Hypertension 2007;50(1):14-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.106.079442.
Lamy C, Oppenheim C, Mas JL. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Handb Clin Neurol 2014;121:1687-701. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-7020-4088-7.00109-7.
Mishra SK, Bhat R, Sudeep K, Nagappa M, Swain A, Badhe A. PRES (posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome) and eclampsia: Review. Internet J Anesth 2008;22(1). [cited 2016 January 10]. Available from: https://www.ispub.com/IJA/22/1/13690.
Matthys LA, Coppage KH, Lambers DS, Barton JR, Sibai BM. Delayed postpartum preeclampsia: An experience of 151 cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;190(5):1464-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2004.02.037.
Sibai BM. Diagnosis, prevention, and management of eclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 2005;105(2):402-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000152351.13671.99.
Huijgen W, van der Kallen B, Boiten J, Lycklama À Nijeholt G. Unilateral reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome after coiling of an aneurysm. J Clin Neurol 2014;10(1):59-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.1.59.
Schneider JP, Krohmer S, Günther A, Zimmer C. Cerebral lesions in acute arterial hypertension: The characteristic MRI in hypertensive encephalopathy [Article in German]. Rofo 2006;178(6):618-26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-926631.
Golombeck SK, Wessig C, Monoranu CM, Schütz A, Solymosi L, Melzer N, et al. Fatal atypical reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: A case report. J Med Case Rep 2013;7:14. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1752-1947-7-14.
Bartynski WS, Zeigler Z, Spearman MP, Lin L, Shadduck RK, Lister J. Etiology of cortical and white matter lesions in cyclosporin-A and FK-506 neurotoxicity. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22(10):1901-14.
Lin JT, Wang SJ, Fuh JL, Hsiao LT, Lirng JF, Chen PM. Prolonged reversible vasospasm in cyclosporin A-induced encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003;24(1):102-4.
Achar SK, Shetty N, Joseph TT. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome at term pregnancy. Indian J Anaesth 2011;55(4):399-401. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/0019-5049.84856.
Schwartz RB, Jones KM, Kalina P, Bajakian RL, Mantello MT, Garada B, et al. Hypertensive encephalopathy: Findings on CT, MR imaging, and SPECT imaging in 14 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1992;159(2):379-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/ajr.159.2.1632361.
Rippe DJ, Edwards MK, Schrodt JF, Bognanno JR, D'Amour PG, Boyko OB. Reversible cerebral lesions associated with tiazofurin usage: MR demonstration. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1988;12(6):1078-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00004728-198811000-00037.
Vaughn DJ, Jarvik JG, Hackney D, Peters S, Stadtmauer EA. High-dose cytarabine neurotoxicity: MR findings during the acute phase. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1993;14(4):1014-6.
Ito Y, Arahata Y, Goto Y, Hirayama M, Nagamutsu M, Yasuda T, et al. Cisplatin neurotoxicity presenting as reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1998;19(3):415-7.
Provenzale JM, Petrella JR, Cruz LC Jr, Wong JC, Engelter S, Barboriak DP. Quantitative assessment of diffusion abnormalities in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22(8):1455-61.
Mukherjee P, McKinstry RC. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: Evaluation with diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 2001;219(3):756-65. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiology.219.3.r01jn48756.
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23(6):1038-48.
Lubarsky SL, Barton JR, Friedman SA, Nasreddine S, Ramadan MK, Sibai BM. Late postpartum eclampsia revisited. Obstet Gynecol 1994;83(4):502-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00006250-199404000-00003.
Altinkaya SO, Nergiz S, Küçük M, Yüksel H, Dayanir Y. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in obstetric patients. Report of three cases with literature review. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2014;41(6):730-3.
Long TR, Hein BD, Brown MJ, Rydberg CH, Wass CT. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome during pregnancy: Seizures in a previously healthy parturient. J Clin Anesth 2007;19(2):145-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2006.07.004.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy. Hypertension in pregnancy. Report of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2013;122(5):1122-31.
Prout RE, Tuckey JP, Giffen NJ. Reversible posterior leucoencephalopathy syndrome in a peripartum patient. Int J Obstet Anesth 2007;16(1):74-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijoa.2006.04.012.
Liman TG, Bohner G, Heuschmann PU, Scheel M, Endres M, Siebert E. Clinical and radiological differences in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome between patients with preeclampsia-eclampsia and other predisposing diseases. Eur J Neurol 2012;19(7):935-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03629.x.
Hefzy HM, Bartynski WS, Boardman JF, Lacomis D. Hemorrhage in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Imaging and clinical features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30(7):1371-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1588.
O'Kane M, Elhalwagy H, Kumar S, Badawi C. Unusual presentation of PRES in the postnatal period. BMJ Case Rep 2014;2014. pii: Bcr2013203406. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-203406.
Pedraza R, Marik PE, Varon J. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: A review. Crit Care Shock 2009;12(4):135-43.
McKinney AM, Short J, Truwit CL, McKinney ZJ, Kozak OS, SantaCruz KS, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Incidence of atypical regions of involvement and imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;189(4):904-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/AJR.07.2024.
Lee SY, Kim SH, Lee SH, Baek HJ, Shon HS, Kim SS. Serial MR spectroscopy in relapsing reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Neurologist 2009;15(6):338-41. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/NRL.0b013e3181914af6.
Alexander AL, Lee JE, Lazar M, Field AS. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 2007;4(3):316-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2007.05.011.
Sonneville R, Klein IF, Wolff M. Update on investigation and management of postinfectious encephalitis. Curr Opin Neurol 2010;23(3):300-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e32833925ec.
Pereira PR, Pinho J, Rodrigues M, Rocha J, Sousa F, Amorim J, et al. Clinical, imagiological and etiological spectrum of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2015;73(1):36-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/0004-282X20140176.
Hamilton BE, Nesbit GM. Delayed CSF enhancement in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29(3):456-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0926.
Benziada-Boudour A, Schmitt E, Kremer S, Foscolo S, Rivière AS, Tisserand M, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: A case of unusual diffusion-weighted MR images. J Neuroradiol 2009;36(2):102-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.2008.08.003.
Stevens CJ, Heran MK. The many faces of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Br J Radiol 2012;85(1020):1566-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1259/bjr/25273221.
Lee VH, Wijdicks EF, Manno EM, Rabinstein AA. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Arch Neurol 2008;65(2):205-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2007.46.
Donmez FY, Basaran C, Kayahan Ulu EM, Yildirim M, Coskun M. MRI features of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in 33 patients. J Neuroimaging 2010;20(1):22-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2008.00306.x.
Doelken M, Lanz S, Rennert J, Alibek S, Richter G, Doerfler A. Differentiation of cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in a patient with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome using diffusion-weighted MRI. Diagn Interv Radiol 2007;13(3):125-8.
Kastrup O, Schlamann M, Moenninghoff C, Forsting M, Goericke S. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: The spectrum of MR imaging patterns. Clin Neuroradiol 2015;25(2):161-71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0293-7.
Demirel I, Kavak BS, Özer AB, Bayar MK, Erhan ÖL. An intensive care approach to posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): An analysis of 7 cases. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc 2014;15(4):217-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.5152/jtgga.2014.14072.
Tan LH, Flower O. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: An important cause of acute severe headache. Emerg Med Int 2012;2012:303152. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/303152.
Miller TR, Shivashankar R, Mossa-Basha M, Gandhi D. Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome, part 1: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical course. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2015;36(8):1392-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4214.
Kühn AL, Huch B, Wendt G, Dooms G, Droste DW. First description of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome as a complication of glycerolnitrate patch following open cardiac surgery. Acta Neurol Scand 2011;124(3):218-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2010.01445.x.
Sheta MA, Paladugu M, Mendelson J, Holland NR. When should nitroglycerine be avoided in hypertensive encephalopathy? Hypertension 2011;58(5):187-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.175703.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2016-05-02
Published 2016-08-02









