The molecular mechanisms of cuproptosis and its relevance to atherosclerosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.11826Keywords:
Cuproptosis, atherosclerosis, AS, copper, tricarboxylic acid cycle, TCA cycle, reactive oxygen species, ROSAbstract
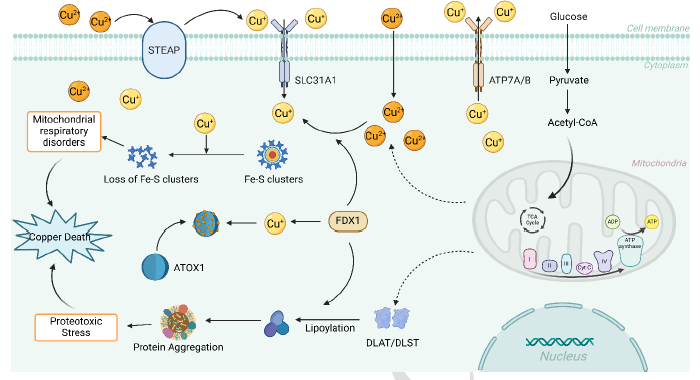
Atherosclerosis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease associated with lipid deposition in the vascular intima. Copper is a vital trace element implicated in the onset and progression of AS. Excessive intracellular copper accumulation induces a unique form of cell death termed “cuproptosis.” The emergence of the concept of cuproptosis has highlighted the potential role of copper in AS. This review explores the regulatory mechanisms of copper metabolism and cuproptosis, summarizes recent findings on the link between copper excess and AS, and examines how cuproptosis may influence AS progression. The goal is to propose novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for AS through the lens of cuproptosis.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Jiankang Wang, Zhian Chen, Hang Shang, Jiajuan Guo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









