Study on the mechanism of Wnt/β-catenin pathway mediated by pterostilbene to reduce cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.11743Keywords:
Pterostilbene, PTE, cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, CIRI, ferroptosis, Wnt/β-catenin pathwayAbstract
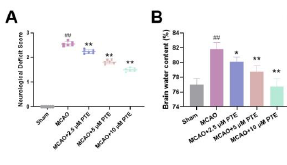
Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI) is the primary cause of damage following ischemic stroke, with ferroptosis serving as a key pathophysiological factor in CIRI. Pterostilbene (PTE) has been shown to reduce cerebral ischemic injury, but whether its mechanism of action involves ferroptosis remains unclear. In this study, an in vitro model of mouse hippocampal neuron (HT22) cell injury and an in vivo mouse CIRI model were established. Treatments included PTE, the ferroptosis activator Erastin, and the Wnt signaling pathway inhibitor (Dkk-1). Cell damage was assessed using flow cytometry, MTT assay, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay, and Calcein-AM/PI staining. Oxidative stress and ferroptosis in cells and tissues were evaluated using biochemical kits and fluorescence staining. Additionally, histopathological staining was performed to assess brain tissue damage, while qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses were used to measure ferroptosis-related factors and Wnt/β-catenin pathway-related proteins in both cells and tissues. HT22 cells subjected to injury exhibited decreased viability and increased cell death (P < 0.05). Similarly, CIRI mice demonstrated pronounced cerebral infarction and neuronal damage. Ferroptosis, characterized by elevated levels of iron ions, lipid peroxides (ROS and MDA), and reduced antioxidant enzymes (GSH and GPX4), was significantly increased in both cells and tissues (P < 0.05). Correspondingly, ferroptosis-related protein levels were elevated (P < 0.05), while Wnt/β-catenin pathway-related protein levels were significantly decreased (P < 0.05). Treatment with Erastin and Dkk-1 exacerbated neuronal damage, intensified ferroptosis, and inhibited the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Conversely, PTE treatment activated the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, reduced ferroptosis, and improved neuronal damage. Specifically, PTE upregulated the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, decreased peroxide accumulation, and antagonized ferroptosis, ultimately mitigating CIRI. These findings suggest that PTE protects against CIRI by modulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and alleviating ferroptosis-induced damage.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yang Jin, Chunwang Fu, Ming Guo, Qiang Yang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









