APOC1 knockdown induces apoptosis and decreases angiogenesis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells through blocking the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.11550Keywords:
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, DLBCL, Apolipoprotein C1, APOC1, human umbilical vein endothelial cells, HUVECs, malignant biological behaviors, angiogenesis, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathwayAbstract
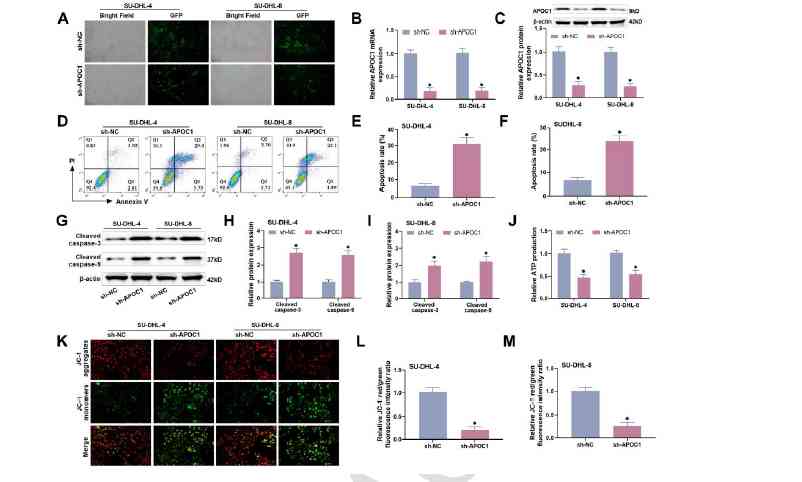
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a highly heterogeneous metastatic lymphoma that can be treated by targeting angiogenesis. Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1) plays a significant role in the proliferation and metastasis of various malignant tumors; however, its role in DLBCL—particularly its effects on angiogenesis—remains largely unexplored. This study investigates the correlation between APOC1 expression and patient prognosis in DLBCL. Using APOC1 gene knockdown, apoptosis, migration, and invasion were assessed through flow cytometry, the EDU assay, wound healing, and Transwell assays. Additionally, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) angiogenesis was evaluated. Advanced techniques, such as immunofluorescence, TUNEL assay, and immunohistochemical labeling were employed to analyze the effects of APOC1 knockdown on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and tumor formation in nude mice. Results showed that APOC1 is overexpressed in DLBCL tissues and cells, with high APOC1 levels associated with poor patient prognosis. In vitro experiments revealed that APOC1 knockdown increased apoptosis and inhibited cell proliferation, migration, invasion, HUVEC angiogenesis, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway protein expression in DLBCL cells. Similarly, in vivo studies demonstrated that APOC1 knockdown significantly reduced tumor growth, angiogenesis-related proteins, and phosphorylated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway proteins in nude mice. APOC1 knockdown promotes apoptosis and suppresses angiogenesis in DLBCL cells by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Jing Gao, Xiaojuan Lu, Guanglei Wang, Tanling Huang, Zhongyu Tuo, Weiwei Meng

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









