Mesenchymal stem cell- derived exosomes as cell-free therapeutics for sensorineural hearing loss
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.11517Keywords:
Sensorineural hearing loss, SNHL, exosomes, inner ear, mesenchymal stem cells, MSCsAbstract
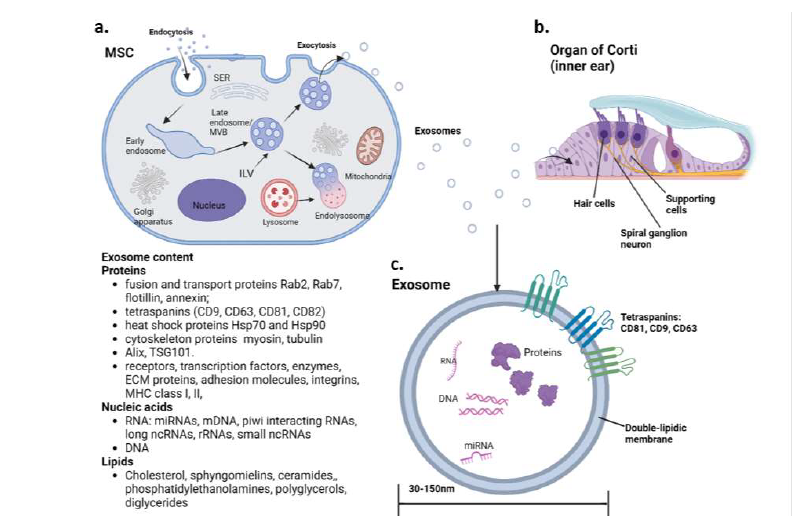
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) can result from various factors, including ototoxic drugs (such as aminoglycosides and chemotherapeutic agents), prolonged exposure to intense sound, and autoimmune or genetic disorders. In adult mammals, the loss of sensory cells in the cochlea is irreversible due to their lack of regenerative capacity. Current treatment options include hearing aids for mild to moderate hearing loss, which rely on residual hearing, and cochlear implants for severe cases, which provide limited auditory recovery while leading to the loss of any remaining natural hearing. Stem cell therapies, particularly those involving mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), are being increasingly explored in regenerative medicine. MSCs are multipotent cells capable of differentiating into mesodermal lineage cells and possess immunomodulatory and regenerative properties, making them potential candidates for SNHL treatment. However, their administration carries risks, including unwanted differentiation, immune system activation, and potential tumorigenic effects. Exosomes, extracellular vesicles in the nanometer size range, are secreted by most eukaryotic cells. These vesicles, which have a double lipid membrane and contain genomic and proteomic material, play a crucial role in intercellular communication. Exosomes derived from MSCs exhibit similar biological functions to their parent cells but with significantly lower risks, as they do not trigger immune responses or pose oncological concerns. This paper aims to review current knowledge on the use of MSCs and MSC-derived exosomes for inner ear sensory cell regeneration and explore their potential for clinical applications.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Maria Perde-Schrepler, Ioana Brie, Alma Maniu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









