Function and mechanism of miRNAs during the process of Klebsiella pneumoniae infection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2025.11421Keywords:
Klebsiella pneumoniae, miRNAs, lung infection, peritonitis, sepsisAbstract
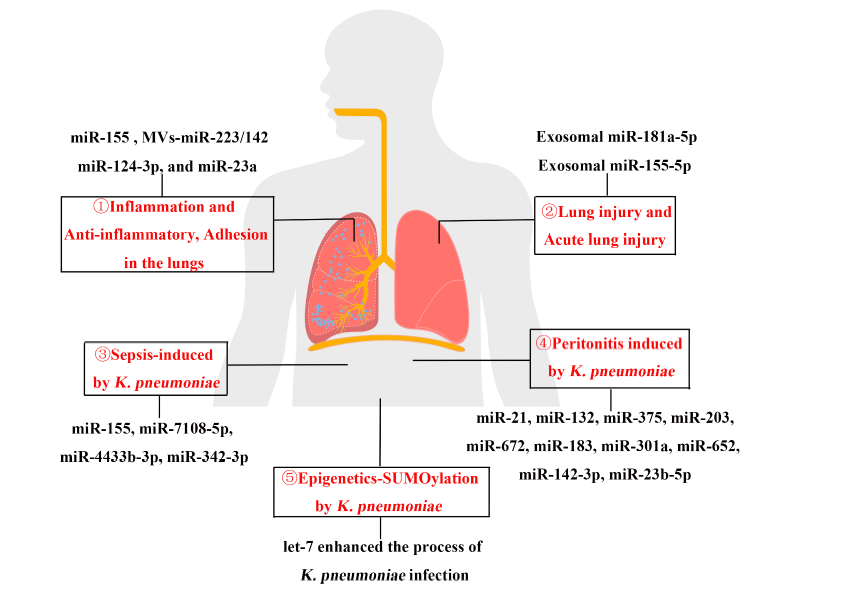
Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae), a Gram-negative bacterium, is a major cause of nosocomial infections and can lead to severe, widespread infections. The rise of hypervirulent and multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae presents significant challenges to public health. Diseases associated with K. pneumoniae, such as pneumonia, lung injury, peritonitis, and sepsis, have garnered increasing attention. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of short, endogenously expressed non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by inhibiting translation or promoting mRNA degradation. As key regulators of gene expression, miRNAs play a crucial role in K. pneumoniae infections by modulating host inflammatory pathways, suppressing inflammasome activity, regulating cytokine secretion, and facilitating post-translational modifications. Understanding miRNA alterations and their mechanisms during K. pneumoniae infections is of great significance. This comprehensive review explores the functions and mechanisms of miRNAs in K. pneumoniae-induced lung injury, peritonitis, and sepsis. By analyzing differential miRNA expression during infection, we aim to provide new insights and potential directions for future clinical diagnosis and treatment strategies for K. pneumoniae infections.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Chuhan Zhang, Ge Li, Safi Ullah, Liang Liu, Huajie Zhao, Fan Yang, Liwei Guo, Duan Li

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









