Histopathologic degenerative score as a predictor of minimal clinically important difference in pain and functionality following surgical treatment for disc herniation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10877Keywords:
Degenerative disc disease, histopathology, intervertebral disc displacement, pain measurement, treatment outcomeAbstract
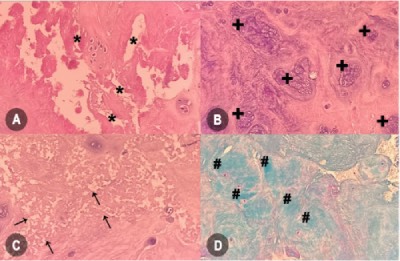
Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) often results in significant pain and disability, and histopathologic (HP) evaluation of intervertebral discs (IVDs) offers critical insights into treatment outcomes. This prospective observational study explores HP changes in IVDs and their association with clinical outcomes following surgical treatment for LDH. A cohort of 141 patients undergoing MRI-confirmed LDH surgery underwent HP evaluation using a semi-quantitative HP degeneration score (HDS). Preoperatively and at a six-month follow-up, the comprehensive clinical assessment included the Oswestry disability index (ODI) and visual analog scale (VAS), with a minimal clinically important difference (MCID) calculated from ODI and VAS. Results indicated significant associations between higher HDS and adverse clinical outcomes, including persistent pain and greater disability post-surgery. Specifically, an HDS ≥ 7 was predictive (OR = 6.25, 95% CI: 2.56–15.23) of disability outcomes measured with MCID-ODI (AUC: 0.692, 95% CI: 0.609–0.767, P < 0.001), and HDS ≥ 8 was predictive (OR = 1.72, 95% CI: 1.04–2.77) of persistent pain measured with MCID-VAS (AUC = 0.628, 95% CI: 0.598–0.737, P = 0.008), highlighting the diagnostic potential of HDS in assessing postoperative recovery. This study underscores the potential of HP evaluation using HDS to provide valuable insights into disease progression and outcomes in LDH patients, complementing conventional radiologic methods. The findings support the application of personalized treatment strategies based on HP findings while acknowledging challenges in interpretation and clinical implementation.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Hakija Bečulić, Emir Begagić, Sabina Šegalo, Fatima Juković Bihorac, Emsel Papić, Ragib Pugonja, Amina Džidić Krivić, Adem Nuhović, Goran Lakičević, Semir Vranić, Mirza Pojskić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









