Research progress on miRNAs function in the interaction between human infectious viruses and hosts: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10821Keywords:
MicroRNAs, virus, virus-host interactionsAbstract
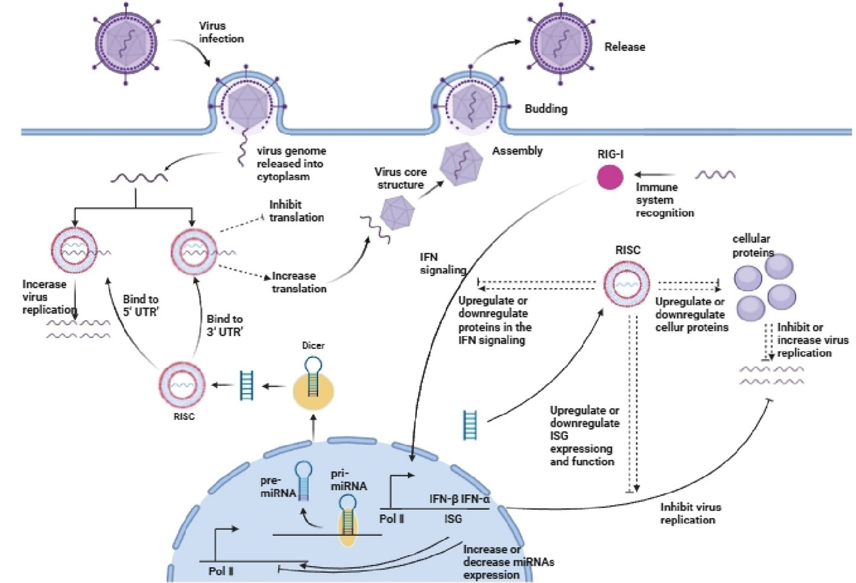
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent a class of non-coding small RNAs that are prevalent in eukaryotes, typically comprising approximately 22 nucleotides, and have the ability to post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression. miRNAs exhibit diverse types and functions, with mechanisms of action that include cell differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, and regulation of signaling pathways. Both viruses and their hosts can encode miRNAs, which serve as crucial effector molecules in the complex interaction between viruses and host cells. Host miRNAs can either directly interact with the virus genome to inhibit virus replication or facilitate virus replication by providing necessary substances. Viral miRNAs can directly bind to host mRNAs, thereby influencing translation efficiency, suppressing the immune response, and ultimately enhancing virus replication. This article comprehensively reviews the roles of miRNAs in virus-host interactions, aiming to provide valuable insights into viral pathogenic mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Xiaotong Wang, Wenchang Zhao

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









